What is PEP 8 ?
Before going into details of PEP 8 the first thing that we need to understand that what exactly is PEP and what is 8 signifies in PEP 8.
PEP contains the index of all Python Enhancement Proposals, known as PEPs. This is an aggregate of documents which explains about information, new features, process and environment settings for python community.
PEP numbers are assigned by the PEP editors, and once assigned are never changed. It signifies the document number.
PEP 8 means Python Enhancement Proposal document number 8 which details about Style Guide for Python Code. This style guide evolves over time as additional conventions are identified and past conventions are rendered obsolete by changes in the language itself.
Although there is no restriction of using all the PEP 8 rule these are good to have as it helps in making code consistency and improve code readability.
You can install, upgrade, uninstall pycodestyle.py (formerly called pep8)with these commands:
$ pip install pycodestyle
$ pip install --upgrade pycodestyle
$ pip uninstall pycodestyle
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Pycodestyle(formerly called pep8) Usage
For demo purpose lets created a test python file with a function to find the max between two numbers find_max.py having content as —
def find_max_number(a:int,b:int)->int:
return a if a>b else b
if __name__ == "__main__":
find_max_number(10,15)
Executing pycodestyle for this file
pycodestyle find_max.py
find_max.py:3:22: E231 missing whitespace after ':'
find_max.py:3:26: E231 missing whitespace after ','
find_max.py:3:28: E231 missing whitespace after ':'
find_max.py:3:33: E225 missing whitespace around operator
find_max.py:4:18: E225 missing whitespace around operator
find_max.py:6:1: E305 expected 2 blank lines after class or function definition, found 1
find_max.py:7:23: E231 missing whitespace after ','
find_max.py:7:27: W292 no newline at end of file
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
In this case we have 8 violations.
As you see above, it outputs the file name which has violations, location, error code and that content.
In order to get output summary of PEP 8 violations we need run the following command pycodestyle --statistics --qq <file_name>
pycodestyle --statistics -qq find_max.py
2 E225 missing whitespace around operator
4 E231 missing whitespace after ':'
1 E305 expected 2 blank lines after class or function definition, found 1
1 W292 no newline at end of file
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
In order to have more details on the voilation we need to use show-source option as pycodestyle --show-source <file_name>
pycodestyle --show-source find_max.py
find_max.py:3:22: E231 missing whitespace after ':'
def find_max_number(a:int,b:int)->int:
^
find_max.py:3:26: E231 missing whitespace after ','
def find_max_number(a:int,b:int)->int:
^
find_max.py:3:28: E231 missing whitespace after ':'
def find_max_number(a:int,b:int)->int:
^
find_max.py:3:33: E225 missing whitespace around operator
def find_max_number(a:int,b:int)->int:
^
find_max.py:4:18: E225 missing whitespace around operator
return a if a>b else b
^
find_max.py:6:1: E305 expected 2 blank lines after class or function definition, found 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
^
find_max.py:7:23: E231 missing whitespace after ','
find_max_number(10,15)
^
find_max.py:7:27: W292 no newline at end of file
find_max_number(10,15)
^
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Moreover you can see the description of how to fix. This is --show-pep8 option.
pycodestyle --show-pep8 find_max.py
find_max.py:3:22: E231 missing whitespace after ':'
Each comma, semicolon or colon should be followed by whitespace.
Okay: [a, b]
Okay: (3,)
Okay: a[1:4]
Okay: a[:4]
Okay: a[1:]
Okay: a[1:4:2]
E231: ['a','b']
E231: foo(bar,baz)
E231: [{'a':'b'}]
find_max.py:3:26: E231 missing whitespace after ','
Each comma, semicolon or colon should be followed by whitespace.
Okay: [a, b]
Okay: (3,)
Okay: a[1:4]
Okay: a[:4]
Okay: a[1:]
Okay: a[1:4:2]
E231: ['a','b']
E231: foo(bar,baz)
E231: [{'a':'b'}]
find_max.py:3:28: E231 missing whitespace after ':'
Each comma, semicolon or colon should be followed by whitespace.
Okay: [a, b]
Okay: (3,)
Okay: a[1:4]
Okay: a[:4]
Okay: a[1:]
Okay: a[1:4:2]
E231: ['a','b']
E231: foo(bar,baz)
E231: [{'a':'b'}]
find_max.py:3:33: E225 missing whitespace around operator
Surround operators with a single space on either side.
- Always surround these binary operators with a single space on
either side: assignment (=), augmented assignment (+=, -= etc.),
comparisons (==, <, >, !=, <=, >=, in, not in, is, is not),
Booleans (and, or, not).
- If operators with different priorities are used, consider adding
whitespace around the operators with the lowest priorities.
Okay: i = i + 1
Okay: submitted += 1
Okay: x = x * 2 - 1
Okay: hypot2 = x * x + y * y
Okay: c = (a + b) * (a - b)
Okay: foo(bar, key='word', *args, **kwargs)
Okay: alpha[:-i]
E225: i=i+1
E225: submitted +=1
E225: x = x /2 - 1
E225: z = x **y
E225: z = 1and 1
E226: c = (a+b) * (a-b)
E226: hypot2 = x*x + y*y
E227: c = a|b
E228: msg = fmt%(errno, errmsg)
find_max.py:4:18: E225 missing whitespace around operator
Surround operators with a single space on either side.
- Always surround these binary operators with a single space on
either side: assignment (=), augmented assignment (+=, -= etc.),
comparisons (==, <, >, !=, <=, >=, in, not in, is, is not),
Booleans (and, or, not).
- If operators with different priorities are used, consider adding
whitespace around the operators with the lowest priorities.
Okay: i = i + 1
Okay: submitted += 1
Okay: x = x * 2 - 1
Okay: hypot2 = x * x + y * y
Okay: c = (a + b) * (a - b)
Okay: foo(bar, key='word', *args, **kwargs)
Okay: alpha[:-i]
E225: i=i+1
E225: submitted +=1
E225: x = x /2 - 1
E225: z = x **y
E225: z = 1and 1
E226: c = (a+b) * (a-b)
E226: hypot2 = x*x + y*y
E227: c = a|b
E228: msg = fmt%(errno, errmsg)
find_max.py:6:1: E305 expected 2 blank lines after class or function definition, found 1
Separate top-level function and class definitions with two blank
lines.
Method definitions inside a class are separated by a single blank
line.
Extra blank lines may be used (sparingly) to separate groups of
related functions. Blank lines may be omitted between a bunch of
related one-liners (e.g. a set of dummy implementations).
Use blank lines in functions, sparingly, to indicate logical
sections.
Okay: def a():n passnnndef b():n pass
Okay: def a():n passnnnasync def b():n pass
Okay: def a():n passnnn# Foon# Barnndef b():n pass
Okay: default = 1nfoo = 1
Okay: classify = 1nfoo = 1
E301: class Foo:n b = 0n def bar():n pass
E302: def a():n passnndef b(n):n pass
E302: def a():n passnnasync def b(n):n pass
E303: def a():n passnnnndef b(n):n pass
E303: def a():nnnn pass
E304: @decoratornndef a():n pass
E305: def a():n passna()
E306: def a():n def b():n passn def c():n pass
find_max.py:7:23: E231 missing whitespace after ','
Each comma, semicolon or colon should be followed by whitespace.
Okay: [a, b]
Okay: (3,)
Okay: a[1:4]
Okay: a[:4]
Okay: a[1:]
Okay: a[1:4:2]
E231: ['a','b']
E231: foo(bar,baz)
E231: [{'a':'b'}]
find_max.py:7:27: W292 no newline at end of file
Trailing blank lines are superfluous.
Okay: spam(1)
W391: spam(1)n
However the last line should end with a new line (warning W292).
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
If we want to exclude specific errors and warning while running pycodestyle we can use the option -ignore and provide the comma separated values of the error codes need to be excluded.
pycodestyle - ignore=E231,E225 find_max.py
find_max.py:6:1: E305 expected 2 blank lines after class or function definition, found 1
find_max.py:7:27: W292 no newline at end of file
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
As we have put E231,E225 in the ignore list the PEP 8 violation count reduced to 2 from 8 which is without ignoring these errors.
PEP 8 Error codes
Code can either denote an error or warning in case of error codes the code start with E followed by a 3 digit number for e.g E101 and for warning code it start with E followed by a 3 digit number for e.g W191.
Below is the classification of error code based on series number.
100 series … (E1 and W1) related to indentation.
200 series … (E2 and W2) related to whitespace.
300 series … (E3 and W3) related to blank lines.
400 series … (E4 and W4) related to imports.
500 series … (E5 and W5) related to line length.
600 series … (E6 and W6) related to deprecation.
700 series … (E7) related to statements.
900 series … (E9) related to syntax errors.
You can refer to official document for more detailing on error code link.
Customization of pep8
We can customise the PEP 8 config to meet our requirement as in we might need to ignore certain errors and warning and also we want to alter the max-line-length etc.
Default user configuration file is in ‘~/.config/pycodestyle‘.
You can write the configuration file as below, this is same as option.
[pep8]
ignore = E231,E225
max-line-length = 160
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
You can specify the configuration file location by--config=<configration_file_location> .
By storing above configuration file in a certain location in respective projects, you can share it in the projects.
At the project level, a setup.cfg file or a tox.ini file is read if present (.pep8 file is also supported, but it is deprecated). If none of these files have a [pep8] section, no project specific configuration is loaded.
Commonly used PEP 8 guidelines
The PEP 8 guidelines can classified in 7 different categories as
Code Lay-out
- Use 4 spaces per indentation level.
- Use spaces not tabs python disallows mixing tabs and spaces for indentation.
- Limit all lines to a maximum of 79 characters.
- Should a line break before or after binary operator? In Python code, it is permissible to break before or after a binary operator, as long as the convention is consistent locally.
- Surround top-level function and class definitions with two blank lines.
- Code in the core Python distribution should always use UTF-8, and should not have an encoding declaration.
Imports should be grouped in the following order:
- Standard library imports.
- Related third party imports.
- Local application/library specific imports.
Wildcard imports (from import *) should be avoided.
Naming Conventions
Naming conventions are the most important pillar in maintaining the code consistency and readability there is as such no rule book to define the naming conventions but PEP 8 has recommendation that is good to follow.
- Never use the characters ‘l’ , ‘O’ , or ‘I’ (uppercase letter eye) as single character variable names. In some fonts, these characters are indistinguishable from the numerals one and zero.
- Class names should normally use the Cap Words (Camel case) convention.
- Variables and function names should have all lowercase letters and underscores to separate words.
- Constant should have all uppercase letters with words separated by underscores
- Use the suffix «Error» on your exception names (if the exception actually is an error).
- Use self for the first argument to instance methods or class methods.
String Quotes
- In Python, single-quoted strings and double-quoted strings are the same. PEP does not make a recommendation for this. Pick a rule and stick to it. When a string contains single or double quote characters, however, use the other one to avoid backslashes in the string. It improves readability.
- Whitespace in Expression and Statement
- Avoid trailing whitespace anywhere. Because it’s usually invisible, it can be confusing: e.g. a backslash followed by a space and a newline does not count as a line continuation marker.
- Always surround these binary operators with a single space on either side: assignment (=), augmented assignment (+=, -= etc.), comparisons (==, <, >, !=, <>, <=, >=, in, not in, is, is not), Booleans (and, or, not).
- Use whitespace to communicate order of operations. x = 12*y + 22*z.
- Avoid excessive whitespace immediately inside of parenthesis, brackets, or braces.
When to use trailing commas
- Trailing commas are usually optional, except they are mandatory when making a tuple of one element. For clarity, it is recommended to surround the latter in parentheses:
# Correct:
FILES = ('setup.cfg',)
# Wrong:
FILES = 'setup.cfg',
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Programming Recommendations
- Comparisons to singletons like None should always be done with is or is not, never the equality operators.
- Use is notoperator rather than not … is for e.g if foo is not None rather than if not foo is None:
- When implementing ordering operations with rich comparisons, it is best to implement all six operations (eq, ne, lt, le, gt, ge) rather than relying on other code to only exercise a particular comparison.
- When catching exceptions, mention specific exceptions whenever possible instead of using a bare except.
- Object type comparisons should always use isinstance() instead of comparing types directly.
Comments
Each line of a block comment starts with a # and a single space.
Use inline comments only if it is unavoidable.
Write docstrings for all public modules, functions, classes, and methods.
Docstrings are not necessary for non-public methods, but you should have a comment that describes what the method does.
For more detailing on the PEP 8 guidelines please check out the official documentation PEP 8 Guidelines
Conclusion
Likewise pycodestyle there is flake8 which is also widely used for checking the code style PEP 8 guidelines in python code. It’s always better to have these plugins in the ide and everytime you save or commit it will highlight the violations.
Maintaining the code style guideline helps in better readability and code consistency. Although it’s a good to have but always prefer to have coding guidelines while writing code.
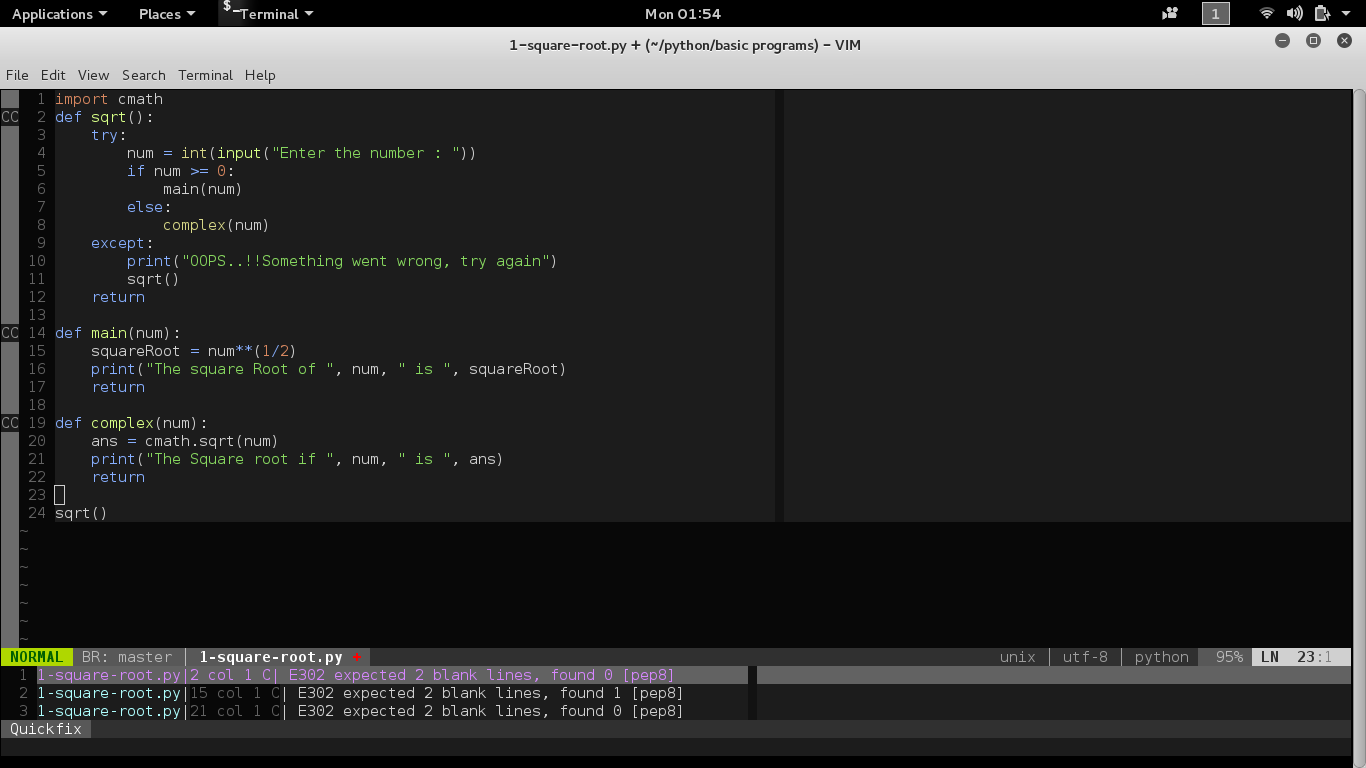
I’m using vim editor as python IDE. Below is a simple python program to calculate square root of a number:
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
squareRoot = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", squareRoot)
return
def complex(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
And the warnings are :
1-square-root.py|2 col 1 C| E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 0 [pep8]
1-square-root.py|15 col 1 C| E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 1 [pep8]
1-square-root.py|21 col 1 C| E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 0 [pep8]
Can you please tell why these warnings are coming?
renatodamas
14.3k6 gold badges33 silver badges47 bronze badges
asked Nov 1, 2015 at 20:30
Amit UpadhyayAmit Upadhyay
7,0114 gold badges43 silver badges56 bronze badges
2
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex_num(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
square_root = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", square_root)
return
def complex_num(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
The previous will fix your PEP8 problems. After your import you need to have 2 new lines before starting your code. Also, between each def foo() you need to have 2 as well.
In your case you had 0 after import, and you had 1 newline between each function. Part of PEP8 you need to have a newline after the end of your code. Unfortunately I don’t know how to show it when I paste your code in here.
Pay attention to the naming, it’s part of PEP8 as well. I changed complex to complex_num to prevent confusion with builtin complex.
In the end, they’re only warning, they can be ignored if needed.
answered Nov 1, 2015 at 21:06
You need to give two blank lines between meaningful code blocks.
These include (for example):
- The import block
- Each function
8bitjunkie
12.6k9 gold badges54 silver badges70 bronze badges
answered Aug 9, 2017 at 9:59
1
Here is the link to the documentation:
PEP8 Style Guide for Python
You should add two spaces between the functions, as shown below:
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex_num(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
square_root = num ** (1 / 2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", square_root)
return
def complex_num(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
answered Aug 9, 2017 at 10:06
1
with warnings:-
import math
def my():
print("hello world")
my()
Without warnings:-
import math
def my():
print("hello world")
my()
Here if you see the two lines space after import statement for second code snippet which will not give any warnings.
Again if you are writing two methods definition you have two give two lines as space between your code block.
answered Aug 9, 2017 at 11:24
All answers seem to be correct. To avoid doing this by hand, you can also use the autopep8 package (pip install autopep8). The result of calling autopep8 filename.py is the same:
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
squareRoot = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", squareRoot)
return
def complex(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
PS: have a look at if __name__ == "__main__":
answered Mar 8, 2018 at 9:48
serv-incserv-inc
34.6k9 gold badges161 silver badges182 bronze badges
Я использую редактор vim в качестве Python IDE. Ниже приведена простая программа python для вычисления квадратного корня числа:
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
squareRoot = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", squareRoot)
return
def complex(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
и предупреждения :
1-square-root.py|2 col 1 C| E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 0 [pep8]
1-square-root.py|15 col 1 C| E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 1 [pep8]
1-square-root.py|21 col 1 C| E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 0 [pep8]
можете ли вы сказать, почему эти предупреждения приходят?
5 ответов
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex_num(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
square_root = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", square_root)
return
def complex_num(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
предыдущий исправит ваш PEP8 проблемы. После импорта необходимо иметь 2 новые строки перед запуском кода. Кроме того, между def foo() вам также нужно иметь 2.
в вашем случае у вас было 0 после импорта, и у вас была 1 новая строка между каждой функцией. Часть PEP8 вам нужно иметь новую строку после окончания кода. К сожалению, я не знаю, как показать это, когда я вставляю ваш код здесь.
обратите внимание на именования, это также часть PEP8. Я изменился complex to complex_num для предотвращения путаницы с builtin complex.
в конце концов, они только предупреждение, их можно игнорировать, если это необходимо.
вот ссылка на документацию:
руководство по стилю PEP8 для Python
Вы должны добавить два пробела между функциями, как показано ниже:
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex_num(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
square_root = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", square_root)
return
def complex_num(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
1
автор: Lakshmikant Deshpande
поскольку python строго следует языку .Вы должны дать два пробела после каждого импорта, а также блок кода.
with warnings:-
import math
def my():
print("hello world")
my()
Without warnings:-
import math
def my():
print("hello world")
my()
здесь, Если вы видите пространство двух строк после инструкции import для второго фрагмента кода, который не будет давать никаких предупреждений.
Опять же, если вы пишете определение двух методов, у вас есть две строки в качестве пространства между вашим блоком кода.
все ответы кажутся правильными. Чтобы избежать этого вручную, вы также можете использовать autopep8 пакета (pip установить autopep8). Результат вызова autopep8 filename.py так же:
import cmath
def sqrt():
try:
num = int(input("Enter the number : "))
if num >= 0:
main(num)
else:
complex(num)
except:
print("OOPS..!!Something went wrong, try again")
sqrt()
return
def main(num):
squareRoot = num**(1/2)
print("The square Root of ", num, " is ", squareRoot)
return
def complex(num):
ans = cmath.sqrt(num)
print("The Square root if ", num, " is ", ans)
return
sqrt()
PS:посмотреть at if __name__ == "__main__":
A list of pylint-errors with reasoning and examples of erroneous and correct code.
Table of contents
- CLI usage
- Stable release
- Dev builds
- List of errors
CLI usage
It’s not required to install CLI util as long as you can navigate list of
errors here or on this
web-site
but you may want to do so.
Stable release
You can install a stable release simply by such commands:
$ python3 -m pip install plerr
$ plerr r1710
For pipx:
$ python3 -m pip install pipx # if not yet installed pipx
$ python3 -m pipx ensurepath # ensure directory where pipx stores apps is on PATH
$ pipx install plerr
$ plerr r1710
Dev builds
In order to use development plerr builds you need to invoke the following commands:
$ git clone https://github.com/vald-phoenix/pylint-errors.git
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y python3-pip # if not yet installed
$ cd pylint-errors
$ python3 setup.py test
$ python3 setup.py install --user
$ python3 -m plerr r1710
pipx users may install the library by
such commands:
$ git clone https://github.com/vald-phoenix/pylint-errors.git
$ sudo apt install -y make python3-pip python3-venv # if not yet installed
$ cd pylint-errors
$ python3 -m pip install pipx wheel # install a package to build a wheel and pipx
$ python3 -m pipx ensurepath # ensure directory where pipx stores apps is on PATH
$ python3 setup.py test # run tests
$ make clean
$ python3 setup.py bdist_wheel # build a binary wheel
$ pipx install dist/* # install a binary wheel by pipx
$ plerr r1710
In order to get the latest updates just git pull origin master and invoke a
command in the root of the project (sudo apt install make if not yet
installed) make rai to install to Python 3 user space site packages or
make raip for pipx.
List of errors
Error codes with [+] mean they’ve got examples of bad and good code.
Rationalisation provided for all entries.
Async Checker Messages
- E1700 (yield-inside-async-function) [+]
- E1701 (not-async-context-manager) [+]
Basic Checker Messages
- C0102 (blacklisted-name) [+]
- C0103 (invalid-name) [+]
- C0112 (empty-docstring) [+]
- C0114 (missing-module-docstring) [+]
- C0115 (missing-class-docstring) [+]
- C0116 (missing-function-docstring) [+]
- C0121 (singleton-comparison) [+]
- C0122 (misplaced-comparison-constant) [+]
- C0123 (unidiomatic-typecheck) [+]
- E0100 (init-is-generator) [+]
- E0101 (return-in-init) [+]
- E0102 (function-redefined) [+]
- E0103 (not-in-loop) [+]
- E0104 (return-outside-function) [+]
- E0105 (yield-outside-function) [+]
- E0106 (return-arg-in-generator)
- E0107 (nonexistent-operator) [+]
- E0108 (duplicate-argument-name) [+]
- E0110 (abstract-class-instantiated) [+]
- E0111 (bad-reversed-sequence) [+]
- E0112 (too-many-star-expressions) [+]
- E0113 (invalid-star-assignment-target) [+]
- E0114 (star-needs-assignment-target) [+]
- E0115 (nonlocal-and-global) [+]
- E0116 (continue-in-finally) [+]
- E0117 (nonlocal-without-binding) [+]
- E0118 (used-prior-global-declaration) [+]
- E0119 (misplaced-format-function) [+]
- R0123 (literal-comparison) [+]
- R0124 (comparison-with-itself) [+]
- W0101 (unreachable) [+]
- W0102 (dangerous-default-value) [+]
- W0104 (pointless-statement) [+]
- W0105 (pointless-string-statement) [+]
- W0106 (expression-not-assigned) [+]
- W0107 (unnecessary-pass) [+]
- W0108 (unnecessary-lambda) [+]
- W0109 (duplicate-key) [+]
- W0111 (assign-to-new-keyword) [+]
- W0120 (useless-else-on-loop) [+]
- W0122 (exec-used) [+]
- W0123 (eval-used) [+]
- W0124 (confusing-with-statement) [+]
- W0125 (using-constant-test)
- W0126 (missing-parentheses-for-call-in-test)
- W0127 (self-assigning-variable) [+]
- W0128 (redeclared-assigned-name)
- W0143 (comparison-with-callable) [+]
- W0150 (lost-exception) [+]
- W0199 (assert-on-tuple) [+]
Broad Try Clause Checker Messages
- W0717 (too-many-try-statements)
Classes Checker Messages
- C0202 (bad-classmethod-argument) [+]
- C0203 (bad-mcs-method-argument) [+]
- C0204 (bad-mcs-classmethod-argument) [+]
- C0205 (single-string-used-for-slots) [+]
- E0202 (method-hidden) [+]
- E0203 (access-member-before-definition) [+]
- E0211 (no-method-argument) [+]
- E0213 (no-self-argument) [+]
- E0236 (invalid-slots-object) [+]
- E0237 (assigning-non-slot) [+]
- E0238 (invalid-slots) [+]
- E0239 (inherit-non-class) [+]
- E0240 (inconsistent-mro) [+]
- E0241 (duplicate-bases) [+]
- E0242 (class-variable-slots-conflict) [+]
- E0301 (non-iterator-returned) [+]
- E0302 (unexpected-special-method-signature) [+]
- E0303 (invalid-length-returned) [+]
- F0202 (method-check-failed)
- R0201 (no-self-use) [+]
- R0202 (no-classmethod-decorator) [+]
- R0203 (no-staticmethod-decorator) [+]
- R0205 (useless-object-inheritance) [+]
- R0206 (property-with-parameters) [+]
- W0201 (attribute-defined-outside-init) [+]
- W0211 (bad-staticmethod-argument) [+]
- W0212 (protected-access) [+]
- W0221 (arguments-differ) [+]
- W0222 (signature-differs)
- W0223 (abstract-method) [+]
- W0231 (super-init-not-called) [+]
- W0232 (no-init) [+]
- W0233 (non-parent-init-called) [+]
- W0235 (useless-super-delegation) [+]
- W0236 (invalid-overridden-method) [+]
Compare-To-Empty-String Checker Messages
- C1901 (compare-to-empty-string) [+]
Compare-To-Zero Checker Messages
- C2001 (compare-to-zero) [+]
Deprecated Builtins Checker Messages
- W0141 (bad-builtin) [+]
Design Checker Messages
- R0901 (too-many-ancestors) [+]
- R0902 (too-many-instance-attributes) [+]
- R0903 (too-few-public-methods) [+]
- R0904 (too-many-public-methods) [+]
- R0911 (too-many-return-statements) [+]
- R0912 (too-many-branches) [+]
- R0913 (too-many-arguments) [+]
- R0914 (too-many-locals) [+]
- R0915 (too-many-statements) [+]
- R0916 (too-many-boolean-expressions) [+]
- R1260 (too-complex) [+]
Docstyle Checker Messages
- C0198 (bad-docstring-quotes) [+]
- C0199 (docstring-first-line-empty) [+]
Else If Used Checker Messages
- R5501 (else-if-used) [+]
Exceptions Checker Messages
- E0701 (bad-except-order) [+]
- E0702 (raising-bad-type) [+]
- E0703 (bad-exception-context) [+]
- E0704 (misplaced-bare-raise) [+]
- E0710 (raising-non-exception) [+]
- E0711 (notimplemented-raised) [+]
- E0712 (catching-non-exception) [+]
- W0702 (bare-except) [+]
- W0703 (broad-except) [+]
- W0705 (duplicate-except) [+]
- W0706 (try-except-raise) [+]
- W0707 (raise-missing-from) [+]
- W0711 (binary-op-exception) [+]
- W0715 (raising-format-tuple) [+]
- W0716 (wrong-exception-operation) [+]
Format Checker Messages
- C0301 (line-too-long) [+]
- C0302 (too-many-lines)
- C0303 (trailing-whitespace) [+]
- C0304 (missing-final-newline)
- C0305 (trailing-newlines)
- C0321 (multiple-statements) [+]
- C0325 (superfluous-parens) [+]
- C0326 (bad-whitespace) [+]
- C0327 (mixed-line-endings)
- C0328 (unexpected-line-ending-format)
- C0330 (bad-continuation)
- W0301 (unnecessary-semicolon) [+]
- W0311 (bad-indentation) [+]
- W0312 (mixed-indentation)
Imports Checker Messages
- C0410 (multiple-imports) [+]
- C0411 (wrong-import-order) [+]
- C0412 (ungrouped-imports) [+]
- C0413 (wrong-import-position) [+]
- C0414 (useless-import-alias) [+]
- C0415 (import-outside-toplevel) [+]
- E0401 (import-error) [+]
- E0402 (relative-beyond-top-level) [+]
- R0401 (cyclic-import) [+]
- W0401 (wildcard-import) [+]
- W0402 (deprecated-module) [+]
- W0404 (reimported) [+]
- W0406 (import-self) [+]
- W0407 (preferred-module) [+]
- W0410 (misplaced-future) [+]
Logging Checker Messages
- E1200 (logging-unsupported-format)
- E1201 (logging-format-truncated) [+]
- E1205 (logging-too-many-args)
- E1206 (logging-too-few-args)
- W1201 (logging-not-lazy) [+]
- W1202 (logging-format-interpolation) [+]
Miscellaneous Checker Messages
- I0023 (use-symbolic-message-instead)
- W0511 (fixme) [+]
Multiple Types Checker Messages
- R0204 (redefined-variable-type)
Newstyle Checker Messages
- E1003 (bad-super-call) [+]
Overlap-Except Checker Messages
- W0714 (overlapping-except)
Parameter Documentation Checker Messages
- W9005 (multiple-constructor-doc) [+]
- W9006 (missing-raises-doc) [+]
- W9008 (redundant-returns-doc)
- W9010 (redundant-yields-doc)
- W9011 (missing-return-doc) [+]
- W9012 (missing-return-type-doc) [+]
- W9013 (missing-yield-doc)
- W9014 (missing-yield-type-doc)
- W9015 (missing-param-doc) [+]
- W9016 (missing-type-doc) [+]
- W9017 (differing-param-doc) [+]
- W9018 (differing-type-doc) [+]
Refactoring Checker Messages
- C0113 (unneeded-not) [+]
- C0200 (consider-using-enumerate) [+]
- C0201 (consider-iterating-dictionary) [+]
- C1801 (len-as-condition) [+]
- R1701 (consider-merging-isinstance)
- R1702 (too-many-nested-blocks)
- R1703 (simplifiable-if-statement) [+]
- R1704 (redefined-argument-from-local) [+]
- R1705 (no-else-return) [+]
- R1706 (consider-using-ternary)
- R1707 (trailing-comma-tuple) [+]
- R1708 (stop-iteration-return) [+]
- R1709 (simplify-boolean-expression)
- R1710 (inconsistent-return-statements) [+]
- R1711 (useless-return) [+]
- R1712 (consider-swap-variables) [+]
- R1713 (consider-using-join) [+]
- R1714 (consider-using-in) [+]
- R1715 (consider-using-get)
- R1716 (chained-comparison) [+]
- R1717 (consider-using-dict-comprehension)
- R1718 (consider-using-set-comprehension)
- R1719 (simplifiable-if-expression) [+]
- R1720 (no-else-raise) [+]
- R1721 (unnecessary-comprehension) [+]
- R1722 (consider-using-sys-exit) [+]
- R1723 (no-else-break) [+]
- R1724 (no-else-continue) [+]
Similarities Checker Messages
- R0801 (duplicate-code)
Spelling Checker Messages
- C0401 (wrong-spelling-in-comment)
- C0402 (wrong-spelling-in-docstring)
- C0403 (invalid-characters-in-docstring)
Stdlib Checker Messages
- E1507 (invalid-envvar-value) [+]
- W1501 (bad-open-mode) [+]
- W1502 (boolean-datetime)
- W1503 (redundant-unittest-assert) [+]
- W1505 (deprecated-method)
- W1506 (bad-thread-instantiation) [+]
- W1507 (shallow-copy-environ) [+]
- W1508 (invalid-envvar-default) [+]
- W1509 (subprocess-popen-preexec-fn) [+]
- W1510 (subprocess-run-check) [+]
String Checker Messages
- E1300 (bad-format-character) [+]
- E1301 (truncated-format-string)
- E1302 (mixed-format-string) [+]
- E1303 (format-needs-mapping)
- E1304 (missing-format-string-key) [+]
- E1305 (too-many-format-args) [+]
- E1306 (too-few-format-args) [+]
- E1307 (bad-string-format-type) [+]
- E1310 (bad-str-strip-call)
- W1300 (bad-format-string-key)
- W1301 (unused-format-string-key)
- W1302 (bad-format-string) [+]
- W1303 (missing-format-argument-key) [+]
- W1304 (unused-format-string-argument) [+]
- W1305 (format-combined-specification) [+]
- W1306 (missing-format-attribute) [+]
- W1307 (invalid-format-index) [+]
- W1308 (duplicate-string-formatting-argument)
- W1401 (anomalous-backslash-in-string)
- W1402 (anomalous-unicode-escape-in-string) [+]
- W1403 (implicit-str-concat-in-sequence)
Typecheck Checker Messages
- E1101 (no-member) [+]
- E1102 (not-callable) [+]
- E1111 (assignment-from-no-return) [+]
- E1120 (no-value-for-parameter) [+]
- E1121 (too-many-function-args) [+]
- E1123 (unexpected-keyword-arg) [+]
- E1124 (redundant-keyword-arg) [+]
- E1125 (missing-kwoa)
- E1126 (invalid-sequence-index) [+]
- E1127 (invalid-slice-index) [+]
- E1128 (assignment-from-none) [+]
- E1129 (not-context-manager) [+]
- E1130 (invalid-unary-operand-type) [+]
- E1131 (unsupported-binary-operation) [+]
- E1132 (repeated-keyword)
- E1133 (not-an-iterable) [+]
- E1134 (not-a-mapping)
- E1135 (unsupported-membership-test) [+]
- E1136 (unsubscriptable-object) [+]
- E1137 (unsupported-assignment-operation) [+]
- E1138 (unsupported-delete-operation) [+]
- E1139 (invalid-metaclass)
- E1140 (unhashable-dict-key) [+]
- E1141 (dict-iter-missing-items) [+]
- I1101 (c-extension-no-member)
- W1113 (keyword-arg-before-vararg) [+]
- W1114 (arguments-out-of-order)
Variables Checker Messages
- E0601 (used-before-assignment) [+]
- E0602 (undefined-variable)
- E0603 (undefined-all-variable) [+]
- E0604 (invalid-all-object) [+]
- E0611 (no-name-in-module) [+]
- E0633 (unpacking-non-sequence) [+]
- W0601 (global-variable-undefined) [+]
- W0602 (global-variable-not-assigned) [+]
- W0603 (global-statement) [+]
- W0604 (global-at-module-level) [+]
- W0611 (unused-import) [+]
- W0612 (unused-variable) [+]
- W0613 (unused-argument) [+]
- W0614 (unused-wildcard-import) [+]
- W0621 (redefined-outer-name) [+]
- W0622 (redefined-builtin) [+]
- W0623 (redefine-in-handler)
- W0631 (undefined-loop-variable) [+]
- W0632 (unbalanced-tuple-unpacking) [+]
- W0640 (cell-var-from-loop) [+]
- W0641 (possibly-unused-variable)
- W0642 (self-cls-assignment)
This site is open source. Improve this page.