[toc]
Problem Statement: How to fix “fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory“?
What is a “fatal” error?
A fatal error causes a program to end with practically no warning without even saving its state. It usually occurs when an application attempts to access a piece of invalid information or data. The program closes down as it shows illegal action, and it returns the user to the operating system. When the fatal error occurs, the user can lose any unsaved changes made in the program.
fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
When does the error occur?
Generally, you face this error when you try to generate the output file while building a shared library using a C extension file. In other words, you encounter this error while trying to build a shared library using the file extension of another language( e.g. C ).
Example: Suppose you use the command below.
gcc -Wall utilsmodule.c -o Utilc
When you execute the above command, you will get the following error message:
utilsmodule.c:1: 20: fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory compilation terminated.
Now that you know the reasons behind the occurrence of the error let’s look at the ways to fix it.
#Fix 1: Using Package Managers According to Your Operating System
Most probably, when you face this error, it’s because you have not installed the static libraries and the header files properly. Hence to solve the error, you need to use the package manager to install them on the PC.
Use the following commands according to the OS installed on your system.
| For Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install python-dev sudo apt-get install python3- dev |
| For Fedora: sudo dnf install python-devel sudo dnf install python3- devel |
| For CentOS: sudo yum install python-devel sudo yum install python3 – devel |
| For Cygwin: apt-cyg install python-devel apt-cyg install python3- devel |
| For openSUSE: sudo zypper in python- devel sudo zypper in python3 -devel |
| For Alpine: sudo apk add python-dev sudo apk add python3 -dev |
Caution: The above command only works if you are using either Python 2 or Python 3 version.
The commands for Python 3.6, 3.8, and 3.9 versions are as follows:
sudo apt install libpython3.6 -devsudo apt install libpython3.8 -devsudo apt install libpython3.9- dev#Fix 2: Ensure that the Python Dev Files Come with Your OS
You can solve this error by checking that the Python dev files come with your operating system. To avoid the fatal error, you should not hard code the library and include paths. However, you can use the pkg-config that will output the correct options for the specific system:
$ pkg-config -- cflags --libs python2-I/usr/include/python2.7 -lpython2.7Also, add the following to the gcc line:
gcc $(pkg-config --cflags --libs python2) -Wall utilsmodule.c -o Utilc#Fix 3: By Changing the Header’s Directory
Sometimes you can solve the “fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory” by simply making changes to the header files. These files are typically installed with Python.
Locating the header files
On Unix os the header files are located in the directories prefix/include/pythonversion/ and exec_prefix/ include/pythonversion/. Here the prefixes are defined using the parameters to the configure script in Python, and the version is '%d.%d' % sys.version_info[:2]. On Windows, the files are installed in prefix/include, where prefix is the installation directory that is specified to the installer.
To find the header file itself, you can use Python 3 configuration:
$ python3-config --include-I/Users/<username>/.pyenv/versions/3.8.2/include/python3.8Generally, the Python development headers are located in the directory shown.
To avoid the error, you must include the headers by placing both the directories on your compiler’s search path for includes. So instead of using the following header directory, which results in a fatal error:
#include "Python.h"Just change the header directory. You can even change it with the following:
#include <python2.7/ Python.h>Using venv
If you are using a virtual environment tool such as venv, then most probably, the Python development headers will already be included in compilation and the linking by default. If it’s not, then you will get an error message:
fatal error: 'Python.h ' file not found #include <Python.h>
If this happens, you must ask the setup.py to search for the header files by setting the CFLAGS. You can now locate the header files and use them with Python setup.py bdist_wheel.
$ CFLAGS = "$(python 3- config -- include)" python setup.py bdist_wheel $ CFLAGS = '-I/path/to/include' python setup.py bdist_wheel
Conclusion
In this article, we learned how to solve the fatal error:Python.h: No such file or directory. I hope this discussion helped you to solve your problem. Please stay tuned and subscribe for more interesting solutions and discussions in the future. Happy learning!
Finxter Computer Science Academy
- One of the most sought-after skills on Fiverr and Upwork is web scraping. Make no mistake: extracting data programmatically from websites is a critical life skill in today’s world that’s shaped by the web and remote work.
- So, do you want to master the art of web scraping using Python’s BeautifulSoup?
- If the answer is yes – this course will take you from beginner to expert in Web Scraping.
I am a professional Python Blogger and Content creator. I have published numerous articles and created courses over a period of time. Presently I am working as a full-time freelancer and I have experience in domains like Python, AWS, DevOps, and Networking.
You can contact me @:
UpWork
LinkedIn
While looking for a solution for the Hungarian problem, I found this GitHub link.
I went through the readme.md file and I performed everything described there. After copying hungarian.so into my working directory, when I tried to compile hungarian.cpp using make hungarian, I got this output:
anupam@JAZZ:~/Python/hungarian-master$ make hungarian
g++ hungarian.cpp -o hungarian
hungarian.cpp:7:20: fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
#include "Python.h"
^
compilation terminated.
make: *** [hungarian] Error 1
I found this related question on Stack Overflow, but the answer didn’t work for me.
I am very new to GitHub I don’t know how to add modules on g++. Can someone help me with that, and what to do next?
Zanna♦
68.2k55 gold badges210 silver badges320 bronze badges
asked Sep 21, 2014 at 14:17
2
For Python 3:
sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev
You can also install it for specific versions of Python (if available for your version of Ubuntu, or from a PPA):
sudo apt-get install python3.4-dev
sudo apt-get install python3.5-dev
The python3-dev package depends on a python3.x-dev package, (where 3.x is the system version of Python) and on the libpython3-dev package, which in turn depends on a corresponding libpython3.x-dev package.
muru
189k52 gold badges460 silver badges711 bronze badges
answered Nov 14, 2015 at 23:15
Martin ThomaMartin Thoma
18k23 gold badges69 silver badges96 bronze badges
This is python code extending with C. No need to use make. Python itself will take care of the cpp code compilation with proper flags.
First you need to have header files and a static library. Install those as,
sudo apt-get install python-dev
Now follow these commands to execute example.py in your code.
python setup.py build
cp build/lib.linux-i686-2.7/hungarian.so .
python example.py
Note: I am using
python2.7, you should take care of your version of python when execute the above commands. It is worth mentioning that you need to installpython-numpyif you not have it as python script need it.
answered Sep 21, 2014 at 14:47
sourav c.sourav c.
43k19 gold badges99 silver badges127 bronze badges
2
- Causes of
'Python.h': No such file or directoryError in C++ - Python Installation That Allows Embedding Its Code in C++
- Steps to Add Python Path to IDE’s
Includeand Linker - Add Python Path to
Includeand Linker - Write Python Codes in C++ and Compile Them
- Conclusion
This article will explain how to solve the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory. This usually happens when we try to embed Python code in C++, but the compiler cannot find a reference to Python inside the system.
Causes of 'Python.h': No such file or directory Error in C++
Below is a C++ program that uses Python codes.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <Python.h>
int main()
{
PyObject* pInt;
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello World from Embedded Python!!!')");
Py_Finalize();
printf("nPress any key to exit...n");
if (!_getch()) _getch();
return 0;
}
When this program is compiled, it gives the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
Build started...
1>------ Build started: Project: Python into Cpp, Configuration: Debug x64 ------
1>1.cpp
1>C:UsersWin 10sourcereposPython into Cpp1.cpp(3,10): fatal error C1083: Cannot open include file: 'Python.h': No such file or directory
1>Done building project "Python into Cpp.vcxproj" -- FAILED.
========== Build: 0 succeeded, 1 failed, 0 up-to-date, 0 skipped ==========
Various reasons cause the 'Python.h': No such file or directory issue.
-
Python is not installed inside the system.
Python is third-party enterprise software that does not come with standard Windows and C++ compilers installation. It must be installed with correct settings and linked to the C++ compiler.
-
C++ compiler cannot find Python.
If the compiler is run through an IDE or mingw4, it can only detect that standard C++ includes packages that come with a standard installation.
Third-party libraries are needed to be added to the IDE
includeand linker files.Three steps need to be executed to solve the above issues.
- Custom installing Python that allows it to be embedded in IDEs.
- Adding Python path to IDE
includeand linker paths. - Writing Python codes inside C++ codes and compiling them.
Python Installation That Allows Embedding Its Code in C++
If there is no Python inside the system, or if it is installed and linked but still the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory occurs, it’s because the Python installation did not download the debug binaries with it.
It is recommended that Python be uninstalled and then reinstalled correctly to solve the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
Head to the Python website and download the latest Python version. If a certain version is required, head to the All Releases download section.
This article demonstrates the steps in Windows OS, so the suitable option is to go with the Windows installer(64bit or 32bit). It is recommended to use the 64-bit version if a modern PC is used.
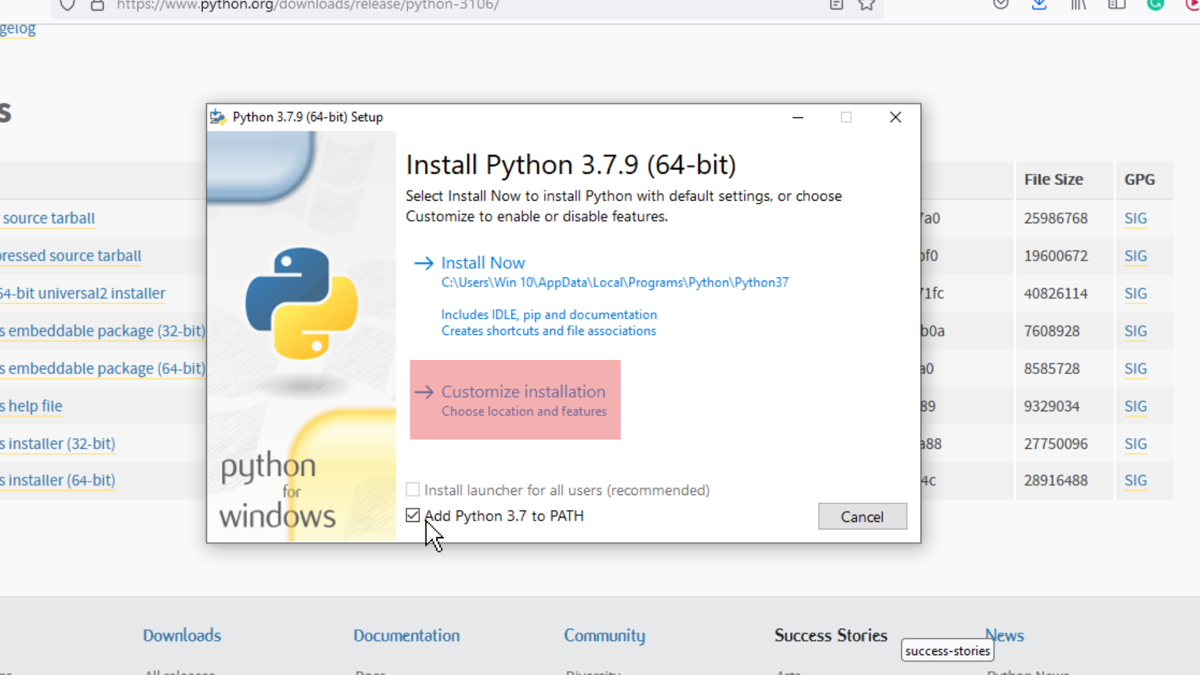
After the download is complete, run the installer, and choose Customize Installation. The Install now option will install Python with default settings but leave the debug binaries out that allows embedding it into IDEs.
Tick the box that asks to Add Python X.X(version) to PATH and then click on Customize Installation.
On the next page, mark all the boxes and then click next.
In the third menu, tick the box Download debug binaries and click on Install. Python will be installed inside the selected directory.
Steps to Add Python Path to IDE’s Include and Linker
Any third-party library that does not come with C++ in its standard installation must be referenced to the IDE. IDEs cannot automatically search and detect third-party libraries inside the system.
This is the reason that causes the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
Though IDE can search for files when the package library is stored in the same directory where the C++ script is located, its path should be mentioned inside the program’s #include<> header.
But storing dependencies this way is a bad practice.
What needs to be done is that the path of the library should be linked to the IDE so that it can be included the way standard header files are included, removing the need to provide a file path with the source code.
Any third-party library that does not come with C++ in its standard installation must be referenced to the IDE. IDEs cannot automatically search and detect third-party libraries inside the system.
This is the reason that causes the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory.
At first, an IDE is needed. It is recommended to go with Visual Studio (2017 or later), and this article will cover the same.
Any other IDE can also be used, the steps are identical in most of them, but Visual Studio makes it simple.
Install Visual Studio in the System
The installer of Visual Studio can be downloaded from here. After downloading the 64-bit Community version, install the software, including the C++ development option.
After installation is completed, create a new project.
The window can look intimidating for readers who have never used Visual Studio before, but there’s no need to worry. Most of the features that will be needed are in front, and this article will guide the rest.
Create a project, and give it a name like ‘Python in cpp’. After the project is created, the main window would look something like this:
If there is just a black screen, press Ctrl+Alt+l, and the solution explorer will open. The solution explorer shows all the files and dependencies available for the project.
Add Python Path to Include and Linker
In this step, the Python path will be included and linked to Visual Studio so that the IDE knows where to look when #include <python.h> is written.
A prerequisite for this step is to know the directory where Python is installed and keep it open in another window. Now head down to Debug > Project Name > Properties (Instead of Project name, it will display the project’s name).
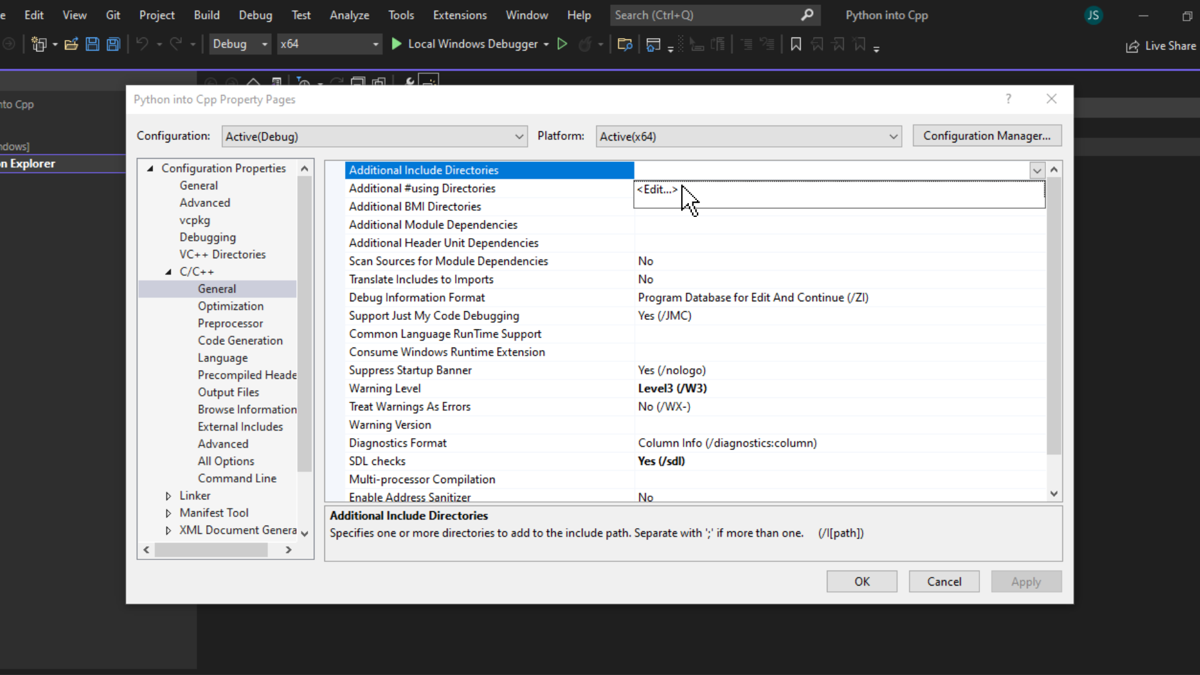
Inside the project properties window, go to C/C++ > General > Additional Include Directories, click on the tiny drop button on the extreme right, and then click on <Edit...>.
The Additional Include Directories dialog box will open. Here, double-click on the first blank space and paste the path of the include folder from the directory where Python is installed inside the system, then click OK.
After the path of include directory is added, head down to Linker > General > Additional Library Directories. Like the previous step, click on <Edit...>.
Now, the libs folder should be added to the linker. This folder is also found inside the Python directory, where the include folder is located.
After it is added, click on OK and then click on Apply.
Write Python Codes in C++ and Compile Them
Once the include and linker paths are added, a sample program must be compiled to check whether the above steps have been executed correctly, and the 'Python.h': No such file or directory error is not encountered again.
Go to the solution explorer and right-click on source files. Click on add > new item, give the file a name and click add.
This new file will contain the code that will be compiled.
Below is the C++ program used at the start of the article that threw errors.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <Python.h>
int main()
{
PyObject* pInt;
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("print('Hello World from Embedded Python!!!')");
Py_Finalize();
printf("nPress any key to exit...n");
if (!_getch()) _getch();
return 0;
}
Now, when the file is compiled by clicking on the green play button on the top, we get the output:
Hello World from Embedded Python!!!
Press any key to exit...
Conclusion
This article explains the steps to solve the error 'Python.h': No such file or directory. After reading this article, the reader can install Python and Visual Studio and link them to the Python library.
Get this book -> Problems on Array: For Interviews and Competitive Programming
In this article, we have explored the reason behind the compilation error «fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory» and presented 3 different fixes to resolve this error.
Table of contents:
- Reason for error
- Fix 1: Install python-dev
- Fix 2: Add include header
- Fix 3: Update compilation command
Reason for error
During compilation of a C or C++ program, you may face the following compilation error:
fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
The reason is that the compiler is not able to locate the required header file Python.h.
The compilation command is usually as follows:
gcc code.c -o code
Fix 1: Install python-dev
The first fix is to re-install python-dev and python3-dev packages in Linux which will reinstall the header files and static/ dynamic libraries in the correct location and fix the error. Use these commands:
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo apt-get install python3-dev
If it does not fix, try installing libpython3.10-dev using the following command:
sudo apt install libpython3.10-dev
Note: change the Python version in the above command accordingly.
If you are using Fedora, use the following command:
sudo dnf install python2-devel
sudo dnf install python3-devel
If you are using OpenSUSE, use the following command:
sudo zypper in python-devel
sudo zypper in python3-devel
If you are using CentOS or RHEL, use the following command:
sudo yum install python-devel
sudo yum install python3-devel
If you are using Alpine, use the following command:
sudo apk add python2-dev
sudo apk add python3-dev
If the header file is in the path /usr/include/python3.10/Python.h, add the following line in your C/ C++ code:
#include <python3.10/Python.h>
We need not specify the entire path as /usr/include is in the INCLUDE path by default.
If you are not sure where the header file is located in your system, use the following command to locate it:
pkg-config --cflags --libs python
If it works correctly and the header file is present in your system, you will get an output like:
-I/usr/include/python3.10 -lpython3.10
Fix 3: Update compilation command
Locate where Python is installed in your system and use the following flags in your compilation command:
-I/usr/include/python3.10 -lpython3.10
This will help the compiler to identify the header files. Following is the updated compilation command:
gcc -I/usr/include/python3.10 -lpython3.10 code.c -o code
Use the following command to locate it where the header file is in your system:
pkg-config --cflags --libs python
If it works correctly and the header file is present in your system, you will get an output like:
-I/usr/include/python3.10 -lpython3.10
We can use the command to get the path directly in the compilation command:
gcc code.c -o code $(pkg-config --cflags --libs python)
With this article at OpenGenus, you must have fixed this error by applying the fixes we presented. Continue with your development.