Давайте рассмотрим обычные и всем нам знакомые ситуации. Например, езду на велосипеде.
Когда велосипедист крутит педали — велосипед едет, а когда не крутит — велосипед начинает тормозить и вскоре останавливается.
Сани, скатившись с горы, постепенно теряют скорость и тоже останавливаются (рисунок 1).
Мы знаем, что причиной всякого изменения скорости движения (в данном случае уменьшения) является сила. Значит, и в рассмотренных примерах на каждое движущееся тело действовала сила.
Существуют разные уже изученные нами ранее силы: сила тяжести, сила упругости, вес тела. В приведенных выше примерах фигурировала сила трения. Именно о ней и пойдет речь на данном уроке.
Что такое сила трения?
Итак, разберем это понятие.
Сила трения — это сила, возникающая при взаимодействии двух тел и препятствующая их относительному движению.
Обозначается она буквой $F$ с индексом, то есть следующим образом: $F_{тр}$.
Взглянем на силу трения на примере движущихся саней (рисунок 2). Она направлена вдоль поверхностей соприкасающихся тел в сторону, противоположную скорости движения тела (саней) по неподвижной поверхности.
Причины возникновения трения
В чем заключаются причины трения?
1. Шероховатость поверхностей тел
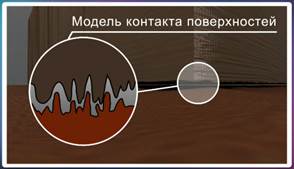
Гладкие на ощупь тела тоже имеют неровности, бугорки и царапины.
С помощью современных лазерных микроскопов сейчас можно увидеть даже самые незаметные неровности. Например, на рисунке 3 вы можете увидеть изображение поверхность листа стали, прошедшего обработку. Для наших невооруженных глаз такой стальной лист будет казаться идеально гладким, но это не так.
Из-за этого, когда одно тело скользит или катится по поверхности другого, эти неровности цепляются друг за друга. Это создает силу, препятствующую движению.
2. Взаимное притяжение молекул соприкасающихся тел
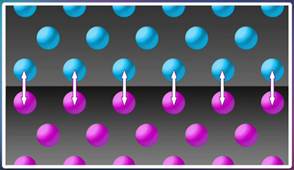
Другая причина возникновения трения — взаимное притяжение молекул соприкасающихся тел. Если поверхности тел идеально гладкие, то при соприкосновении молекулы тел находятся очень близко друг к другу. В этом случае заметно проявляется притяжение между молекулами тел (рисунок 4).
Изменение силы трения. Смазка
Силу трения можно уменьшить во много раз, если ввести между трущимися поверхностями смазку. Ее слой разъединит поверхности трущихся тел (рисунок 5).
Как смазка влияет на силу трения?
В этом случае соприкасаются не поверхности тел, а слои смазки. Смазка же в большинстве случаев жидкая, а, как известно, трение жидких слоев меньше, чем твердых.
Например, на коньках малое трение при скольжении по льду объясняется также действием смазки. Смазкой в этом случае является вода, образующаяся между коньками и льдом тонким слоем.
Именно из-за маленького трения жидкости мы поскальзываемся на вымытом полу. А в технике благодаря меньшему трению жидкости в качестве смазки широко применяют различные масла.
Виды трения
Какие виды трения вы знаете?
Если одно тело скользит по поверхности второго, то возникает особое трение — трение скольжения. Оно возникает, например, при движении саней или лыж по снегу, при скольжении коньков по льду (рисунок 6).
Если же первое тело не скользит, а катится по поверхности второго, то возникающее при этом трение называют иначе — трением качения.
Оно проявляется при перекатывании бревна или бочки по земле, при движении автомобиля, велосипеда и других транспортных средств на колесах (рисунок 7).
Измерение силы трения
Силу трения можно не только изменить, применяя смазку, как было сказано ранее, но еще и измерить.
Как можно измерить силу трения?
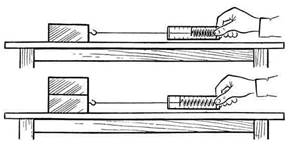
Возьмем деревянный брусок и прикрепим к нему динамометр. Теперь будем его двигать, держа динамометр горизонтально (рисунок 8, а). Что покажет прибор?
На брусок в горизонтальном направлении действуют две силы. Это сила упругости пружины динамометра, направленная в cторону движения, и сила трения, направленная против движения.
Брусок движется равномерно, значит эти две силы компенсируют друг-друга (их равнодействующая равна 0). Следовательно, эти две силы равны по модулю, но имеют разные направления.
Таким образом, динамометр показывает силу, равную по модулю силе трения.
Измеряя силу, с которой динамометр действует на тело при равномерном движении, мы измеряем силу трения.
Как показать, что сила трения зависит от силы, прижимающей тело к поверхности?
Какие сани легче тащить: с грузом или без? Конечно, с грузом.
Также если мы положим на наш брусок какой-нибудь груз, и таким же образом измерим силу трения, то увидим, что она больше, чем у бруска без груза.
Чем больше сила, прижимающая тело к поверхности, тем больше возникающая при этом сила трения.
Как показать на опыте, что при равных нагрузках сила трения скольжения больше силы трения качения?
Положив брусок на круглые палочки (рисунок 8, б), мы измерим силу трения качения. Она будет меньше силы трения скольжения.
При равных нагрузках сила трения качения всегда меньше силы трения скольжения.
Именно поэтому мы повсеместно используем колесо, ведь оно помогает «заменить» силу трения скольжения на намного меньшую силу трения качения.
Упражнение
Лыжник спускается с горы и далее скользит по горизонтальной лыжне. На рисунке 9 изобразите силу трения и точку ее приложения.
Посмотреть ответ
Скрыть
На рисунке 10 изображена сила трения. Она возникает между соприкасающимися телами (лыжами и снежной поверхностью) и направлена в сторону, противоположную движению лыжника.
The force that acts between two bodies which are sliding or trying to slide against each other is known as friction. For example, when we push a box along a rough floor, friction is responsible for making the task difficult.
Friction is also known as an opposing force since it always acts in the opposite direction of a body that is moving or trying to move. A moving body is slowed down due to the virtue of friction. At times, friction is useful since it stops car tires from skidding on the road and also helps us to walk on the pavement without slipping. While walking, the friction caused between the tread on shoes and the ground prevents us from slipping.
Sometimes, too much friction is unnecessary, and we want to reduce friction. For example, friction between machine parts reduces the efficiency of the machine and in order to reduce this friction, we oil the machine parts. Oil helps to separate the surfaces and this helps to reduce the friction between them.
Factors affecting Friction
There are many factors that affect the frictional conditions at the interface between two surfaces in relative motion. These factors are as follows:
- Surface Finish- The frictional coefficient is drastically affected by the roughness, number, and even the directional contact points of the asperities on the surfaces.
- Temperature- The overall level of cold or heat or cold in an environment can affect friction. For example, temperature determines whether an anti-wear or extreme pressure additive will be effective in certain applications.
- Operational Load- Friction varies directly with the load. A load that exceeds the designed capacity will drastically increase the frictional coefficient of friction.
- Relative Speed- Increasing the speed beyond the specified safety level will dramatically increase friction.
- Nature of the Relative Motion between the Surfaces- The frictional coefficient is also affected by the sliding motion versus the rolling motion.
Methods of Increasing Friction
Method 1: Create an uneven or rugged or adhesive point of contact. When two or more bodies either slide or rub against each other, there are three things that may happen: small irregularities, nooks, and crannies on the surfaces can catch on each other; one or both the surfaces can deform due to motion; and lastly, the atoms within each surface can interact with each other. Practically, all three of these effects do the same thing: generate friction. An adhesive interaction with other surfaces (like tacky glue, etc.) is an easy way to increase friction.
Method 2: Pressing the two surfaces together harder. A fundamental principle of basic physics is that the friction experienced by a body is directly proportional to its normal force. This implies that we can increase the friction between two surfaces can be increased if we press the surfaces into each other with a greater force.
Method 3: Stopping any relative motion. That is, if one body is in motion with respect to another body, stop it. Until now, we have focused on sliding friction, which is also known as kinetic friction-the friction that occurs between two bodies as they slide against one another. In fact, this friction is different from static friction, which occurs when a body just starts to move against one another. The friction between two bodies is the highest right when they start moving against one another. This friction decreases, once they are gradually in motion. This is one of the most important reasons why it’s harder to start pushing a heavy body than it is to keep it moving.
Method 4: Remove lubrication between the two surfaces. Oil, grease, petroleum jelly, etc. are lubricants that can greatly reduce the friction between two objects or surfaces. This is due to the fact that friction between two solids is much higher than the friction between those solids and the liquid between them. To increase friction, we need to remove any lubricants from the scenario, using only dry and un-lubricated parts to generate friction.
Method 5: Increase the fluid viscosity. Besides solid objects, fluids (liquids) and gases (like air) can also generate friction. The amount of friction generated by a fluid as it passes against a solid depends on several factors. One of the easiest of these to control is the fluid viscosity since the greater the viscosity of the liquid, the greater is the friction between the fluid and the solid. The highly viscous fluids (ones that are “thick”, “gooey”, etc.) generate more friction than fluids that are less viscous (ones that are “smooth” and “liquid”).
Method 6: Increase the area exposed to air. As noted in the previous point, fluids like water and air can generate friction as they move against solid objects. The frictional force that an object experiences as it moves through a fluid is called drag. One of the most important properties of drag is that objects with bigger surface area, to the fluid as they move through it — have a greater drag.
Method 7: Use a shape that has a greater drag coefficient. A variety of shapes interact with fluids in a variety of ways as they pass through them — this implies that some shapes can have greater drag than other shapes that are made out of the same amount of material. The drag coefficient is the quantity that measures the relative amount of drag a shape makes hence shapes with high drags are said to have high drag coefficients.
Method 8: Use a less permeable material. Some materials are permeable to fluids. In Layman’s terms, they have holes in them that allow the fluid to pass through them. This readily reduces the area of the object that the fluid is able to push against and this lowers the force of drag. This property holds even if they are microscopic holes — as long as the holes are large enough to let some of the fluid pass through the object, the drag will be reduced. This is why parachutes which are designed to produce lots of drag to slow the speed of the user’s fall, are made out of strong, light silk or nylon and not cheesecloth or coffee filters.
Method 9: Increase the speed of the object. It does not matter what the shape of an object it is or how less/more permeable the material it’s made from is, the drag which it creates will always increase as it goes faster. The faster a body moves, the more fluid it has to move through, and, thus, the greater drag it experiences. Bodies moving at very high speeds will experience very high friction due to drag, so these objects must be streamlined or else they will fall apart under the force of the drag.
Methods of Reducing Friction
Method 1: Objects that move in fluids such as boats, planes, cars, etc, the shape of their body must be streamlined in order to reduce the friction between the bodies of the objects as the fluid.
Method 2: Friction can be reduced by polishing the surface of a body as polishing makes the surface smooth and even.
Method 3: Lubricants such as oil or grease must be applied to machine parts regularly to reduce the friction between them.
Method 4: Suppose an object is rolled over a surface, the friction between the rolled object and surface can be reduced by using ball bearings.
Method 5: Friction between two surfaces can also be reduced by reducing the contact between the surfaces.
Method 6: Ball bearings are used in manufacturing vehicles, bicycles, and vehicles to reduce friction.
Sample Questions on Friction
Question 1: What happens when you decrease the amount of friction?
Answer:
Less friction means it is harder to stop. The low friction scenario occurs to cars when it rains. That’s why there are often so many accidents. Even though the friction of the brakes is still present, the brakes may be wet, and the wheels are not in as much contact with the ground surface.
Question 2: What are 3 ways friction can be reduced?
Answer:
Polishing the rough surface. Adding bearings or wheels between the moving parts of a machine or vehicles reduce friction and allow smooth movement as rolling friction is less than sliding friction.
Question 3: Can we reduce friction to zero?
Answer:
Friction can be reduced to a great extent by polishing surfaces or by using a large amount of lubricants such as oil, water, or grease but we cannot reduce friction to zero. We cannot completely eliminate friction as it is necessary for any motion without it we cannot imagine any motion as there is no motion on a smooth surface.
Question 4: On what factors friction depends?
Answer:
Friction mainly depends on two factors: 1) the material that is in contact with the body 2) the force which is pushing the two bodies together
Question 5: Does friction depend on mass?
Answer:
Friction DOES NOT depend on the mass of the body. It only depends on the normal force and the roughness of the surface in contact as it is generated during actual contact only.
Question 6: What do we call the substance that is used to reduce friction?
Answer:
A lubricant is generally an organic substance, introduced to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. Therefore it helps to reduce friction and make the motion easier.
The force that acts between two bodies which are sliding or trying to slide against each other is known as friction. For example, when we push a box along a rough floor, friction is responsible for making the task difficult.
Friction is also known as an opposing force since it always acts in the opposite direction of a body that is moving or trying to move. A moving body is slowed down due to the virtue of friction. At times, friction is useful since it stops car tires from skidding on the road and also helps us to walk on the pavement without slipping. While walking, the friction caused between the tread on shoes and the ground prevents us from slipping.
Sometimes, too much friction is unnecessary, and we want to reduce friction. For example, friction between machine parts reduces the efficiency of the machine and in order to reduce this friction, we oil the machine parts. Oil helps to separate the surfaces and this helps to reduce the friction between them.
Factors affecting Friction
There are many factors that affect the frictional conditions at the interface between two surfaces in relative motion. These factors are as follows:
- Surface Finish- The frictional coefficient is drastically affected by the roughness, number, and even the directional contact points of the asperities on the surfaces.
- Temperature- The overall level of cold or heat or cold in an environment can affect friction. For example, temperature determines whether an anti-wear or extreme pressure additive will be effective in certain applications.
- Operational Load- Friction varies directly with the load. A load that exceeds the designed capacity will drastically increase the frictional coefficient of friction.
- Relative Speed- Increasing the speed beyond the specified safety level will dramatically increase friction.
- Nature of the Relative Motion between the Surfaces- The frictional coefficient is also affected by the sliding motion versus the rolling motion.
Methods of Increasing Friction
Method 1: Create an uneven or rugged or adhesive point of contact. When two or more bodies either slide or rub against each other, there are three things that may happen: small irregularities, nooks, and crannies on the surfaces can catch on each other; one or both the surfaces can deform due to motion; and lastly, the atoms within each surface can interact with each other. Practically, all three of these effects do the same thing: generate friction. An adhesive interaction with other surfaces (like tacky glue, etc.) is an easy way to increase friction.
Method 2: Pressing the two surfaces together harder. A fundamental principle of basic physics is that the friction experienced by a body is directly proportional to its normal force. This implies that we can increase the friction between two surfaces can be increased if we press the surfaces into each other with a greater force.
Method 3: Stopping any relative motion. That is, if one body is in motion with respect to another body, stop it. Until now, we have focused on sliding friction, which is also known as kinetic friction-the friction that occurs between two bodies as they slide against one another. In fact, this friction is different from static friction, which occurs when a body just starts to move against one another. The friction between two bodies is the highest right when they start moving against one another. This friction decreases, once they are gradually in motion. This is one of the most important reasons why it’s harder to start pushing a heavy body than it is to keep it moving.
Method 4: Remove lubrication between the two surfaces. Oil, grease, petroleum jelly, etc. are lubricants that can greatly reduce the friction between two objects or surfaces. This is due to the fact that friction between two solids is much higher than the friction between those solids and the liquid between them. To increase friction, we need to remove any lubricants from the scenario, using only dry and un-lubricated parts to generate friction.
Method 5: Increase the fluid viscosity. Besides solid objects, fluids (liquids) and gases (like air) can also generate friction. The amount of friction generated by a fluid as it passes against a solid depends on several factors. One of the easiest of these to control is the fluid viscosity since the greater the viscosity of the liquid, the greater is the friction between the fluid and the solid. The highly viscous fluids (ones that are “thick”, “gooey”, etc.) generate more friction than fluids that are less viscous (ones that are “smooth” and “liquid”).
Method 6: Increase the area exposed to air. As noted in the previous point, fluids like water and air can generate friction as they move against solid objects. The frictional force that an object experiences as it moves through a fluid is called drag. One of the most important properties of drag is that objects with bigger surface area, to the fluid as they move through it — have a greater drag.
Method 7: Use a shape that has a greater drag coefficient. A variety of shapes interact with fluids in a variety of ways as they pass through them — this implies that some shapes can have greater drag than other shapes that are made out of the same amount of material. The drag coefficient is the quantity that measures the relative amount of drag a shape makes hence shapes with high drags are said to have high drag coefficients.
Method 8: Use a less permeable material. Some materials are permeable to fluids. In Layman’s terms, they have holes in them that allow the fluid to pass through them. This readily reduces the area of the object that the fluid is able to push against and this lowers the force of drag. This property holds even if they are microscopic holes — as long as the holes are large enough to let some of the fluid pass through the object, the drag will be reduced. This is why parachutes which are designed to produce lots of drag to slow the speed of the user’s fall, are made out of strong, light silk or nylon and not cheesecloth or coffee filters.
Method 9: Increase the speed of the object. It does not matter what the shape of an object it is or how less/more permeable the material it’s made from is, the drag which it creates will always increase as it goes faster. The faster a body moves, the more fluid it has to move through, and, thus, the greater drag it experiences. Bodies moving at very high speeds will experience very high friction due to drag, so these objects must be streamlined or else they will fall apart under the force of the drag.
Methods of Reducing Friction
Method 1: Objects that move in fluids such as boats, planes, cars, etc, the shape of their body must be streamlined in order to reduce the friction between the bodies of the objects as the fluid.
Method 2: Friction can be reduced by polishing the surface of a body as polishing makes the surface smooth and even.
Method 3: Lubricants such as oil or grease must be applied to machine parts regularly to reduce the friction between them.
Method 4: Suppose an object is rolled over a surface, the friction between the rolled object and surface can be reduced by using ball bearings.
Method 5: Friction between two surfaces can also be reduced by reducing the contact between the surfaces.
Method 6: Ball bearings are used in manufacturing vehicles, bicycles, and vehicles to reduce friction.
Sample Questions on Friction
Question 1: What happens when you decrease the amount of friction?
Answer:
Less friction means it is harder to stop. The low friction scenario occurs to cars when it rains. That’s why there are often so many accidents. Even though the friction of the brakes is still present, the brakes may be wet, and the wheels are not in as much contact with the ground surface.
Question 2: What are 3 ways friction can be reduced?
Answer:
Polishing the rough surface. Adding bearings or wheels between the moving parts of a machine or vehicles reduce friction and allow smooth movement as rolling friction is less than sliding friction.
Question 3: Can we reduce friction to zero?
Answer:
Friction can be reduced to a great extent by polishing surfaces or by using a large amount of lubricants such as oil, water, or grease but we cannot reduce friction to zero. We cannot completely eliminate friction as it is necessary for any motion without it we cannot imagine any motion as there is no motion on a smooth surface.
Question 4: On what factors friction depends?
Answer:
Friction mainly depends on two factors: 1) the material that is in contact with the body 2) the force which is pushing the two bodies together
Question 5: Does friction depend on mass?
Answer:
Friction DOES NOT depend on the mass of the body. It only depends on the normal force and the roughness of the surface in contact as it is generated during actual contact only.
Question 6: What do we call the substance that is used to reduce friction?
Answer:
A lubricant is generally an organic substance, introduced to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. Therefore it helps to reduce friction and make the motion easier.
1. Причины возникновения силы трения
Сила трения возникает между поверхностями двух взаимодействующих тел. Если одно тело движется по поверхности другого, сила трения всегда направлена против движения. Рассмотрим эту ситуацию подробнее.
Часто приходится слышать фразы: «Не сотри ноги!», «Сотри, пожалуйста, с доски!». Что при этом имеется в виду? Какое явление скрывается за подобными фразами?
Когда поверхность одного тела движется по поверхности другого тела, то, даже если нам не видны бугорки, трещины, царапины, неровности – шероховатости на поверхностях тел, они начинают задевать друг за друга. Это и есть одна из причин возникновения силы трения (Рис. 1).
Рис. 1. Шероховатости на поверхностях тел – первая причина появления силы трения
Существует еще одна причина, по которой появляется сила трения. Опыт показал, что если начать устранять неровности на поверхностях трущихся тел, тщательно шлифуя их, то вначале сила трения, как и ожидается, будет уменьшаться. Но когда поверхности тел будут приближаться к идеально гладким, сила трения резко возрастет, тела начнут буквально прилипать друг к другу. Это происходит потому, что молекулы идеально гладких поверхностей начинают располагаться настолько близко друг к другу, что между ними начинают действовать силы взаимного притяжения (Рис. 2).
Рис. 2. Взаимное притяжение молекул – вторая причина появления силы трения
На практике чаще всего приходится сталкиваться с силой трения, вызванной шероховатостями на поверхностях тел.
2. Трение скольжения
Заставим брусок скользить по поверхности стола, действуя на него горизонтально направленной силой.
Сила трения скольжения возникает при скольжении одного тела по поверхности другого.
Для измерения этой силы воспользуется динамометром. Если перемещать тело равномерно, то сила упругости пружины динамометра (то есть показания прибора) будет равняться силе трения скольжения, действующей на брусок со стороны стола (Рис. 3).
Силу трения можно увеличить, положив на брусок нагрузку (например, гирю или другой брусок).
Рис. 3. Измерение силы трения
Оказывается, что силу трения скольжения можно изменить, изменив материал трущихся поверхностей или способ их обработки (шлифовка, полировка, или, наоборот, создание искусственной шероховатости, как на подошвах спортивной обуви или на автомобильных покрышках). Например, положив на стол под бруски наждачную бумагу можно заметить значительное увеличение силы трения.
Итак, сила трения скольжения зависит:
· от нагрузки;
· от качества обработки поверхностей взаимодействующих тел.
3. Трение качения
Часто в различных механизмах, да и просто в быту стараются заменить трение скольжения трением качения.
Сила трения качения возникает при качении одного тела по поверхности другого.
Оказывается, при прочих равных условиях сила трения качения в десятки и сотни раз меньше силы трения скольжения (Рис. 4).
Рис. 4. Сила трения качения значительно меньше силы трения скольжения
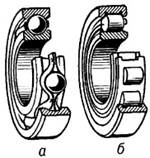
Этот факт используется в подшипниках качения (шариковых и роликовых) (Рис. 5).
Рис. 5. Шариковый (а) и роликовый (б) подшипники качения
4. Трение покоя
Разместим на горизонтальном столе тело и, пользуясь динамометром, начнем действовать на тело все увеличивающейся горизонтальной силой. До некоторых пор груз будет оставаться неподвижным. Следовательно, на груз действует сила, компенсирующая силу упругости пружины динамометра. Это и есть сила трения покоя (Рис. 6).
Сила трения покоя возникает при действии на неподвижное тело силы, направленной параллельно поверхности контакта этого тела с другим телом.
Рис. 6. Брусок остается неподвижным благодаря силе трения покоя
У силы трения покоя есть максимальное значение. Если увеличить силу натяжения пружины динамометра до этого максимального значения, тело придет в движение, а трение покоя сменится трением скольжения.
Трение покоя – своеобразный «страж» состояния покоя. Именно благодаря трению покоя предметы не скользят по поверхности стола, мебель – по поверхности пола. Нитки, из которых соткана наша одежда, каждая находится на своем месте, и ткань сохраняет свою целостность. Узлы не распускаются сами по себе, а наши ноги не скользят по поверхности Земли.
5. Управление величиной силы трения
Очень часто приходится рассматривать вопрос об увеличении или об уменьшении трения в тех случаях, когда оно полезно, или, наоборот, вредно.
Рассмотрим различные способы изменения величины силы трения, опираясь на известные пословицы и поговорки.
«Баба с воза – кобыле легче». Если уменьшить величину нагрузки, то сила трения станет меньше.
«Готовь сани летом, а телегу зимой». В данном случае идет речь о замене трения скольжения на трение качения.
«Плуг от работы блестит». Здесь можно вспомнить, что при скольжении по менее шероховатой (блестящей) поверхности сила трения меньше.
«Не подмажешь – не поедешь». Хотя эту ситуацию мы еще не рассматривали, но вы знаете, что и в быту, и в технике для уменьшения трения очень часто используются различные смазочные материалы. Слой жидкой смазки, располагаясь между трущимися поверхностями, значительно уменьшает силу трения. Именно об этом и говорится в данной поговорке.
Итак, подводя итоги, можно сказать, что величина силы трения зависит от:
· вида трения (трение скольжения или качения);
· нагрузки;
· качества обработки поверхностей;
· использования смазочных материалов.
Теперь, когда вы изучили свойства силы трения, попробуйте облегчить задачу своим друзьям или членам семьи в следующей ситуации. Требуется передвинуть из одного угла комнаты в другой тяжелый шкаф. Что вы посоветуете?
Как можно увеличить силу трения
На первый взгляд, излишняя сила трения вредна. Она уменьшает КПД механизмов, изнашивает детали. Но есть случаи, когда силу трения необходимо увеличить. Например, при качении колес необходимо улучшить их сцепление с дорогой. Посмотрите, каким образом это можно сделать.

Инструкция
Чтобы понять, как увеличить силу трения, вспомните, от чего она зависит. Рассмотрите формулу: Fтр=мN, где м – коэффициент трения, N – сила реакции опоры, Н. Сила реакции опоры, в свою очередь, зависит от массы: N=G=mg, где G — вес тела, Н; m – масса тела, кг; g – ускорение свободного падения, м/с2.
Из формулы можно сделать вывод, что сила трения зависит от коэффициента трения. Коэффициент трения определяется для каждой пары взаимодействующих материалов и зависит от природы материала и качества поверхности.
Таким образом, первый способ увеличить трение – изменить материал скользящей поверхности. Наверное, вы замечали, что в одной обуви практически невозможно передвигаться по влажному кафельному полу, а в другой вы не ощущаете каких-либо неудобств. Это объясняется тем, что подошвы ботинок сделаны из различных материалов. Скользкая обувь имеет низкий коэффициент трения скольжения подошвы относительно влажного кафеля.
Второй способ – увеличить шероховатость поверхности. Пример — зимние шины для автомобиля имеют более рельефный протектор, чем летние. За счет этого на скользкой зимней дороге автомобиль может уверенно двигаться.
Третий способ – увеличение массы. Как видно из формулы, сила трения напрямую зависит от массы. Это объясняет, почему груженому автомобилю в отдельных случаях легче выбраться из грязи, чем тому, что налегке. Это правило работает при определенном качестве грунта – в вязкую, болотистую почву тяжелая машина просядет больше, чем легкая.
Четвертый способ – удаление смазки. Представьте транспортер технологической линии, состоящий из вращающихся валиков, на которые натянута лента. Валики транспортера начинают проскальзывать по ленте, если они загрязнены. В этом случае грязь действует как смазка. Очистив детали механизма, вы увеличите силу трения и повысите КПД оборудования.
Пятый способ – полировка. Отполировав поверхность, вы можете увеличить силу трения. Это объясняется тем, что при соприкосновении отполированных поверхностей включаются силы межмолекулярного притяжения. Например, очень трудно раздвинуть два листа стекла, сложенных вместе.
Видео по теме
Источники:
- как изменится сила трения скольжения при
Войти на сайт
или
Забыли пароль?
Еще не зарегистрированы?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.