Troubleshooting WSUS 3.0 SP2 on Windows Server – In the post we will see steps to troubleshoot WSUS 3.0 SP2 related issues. We will see the most common issues related to WSUS 3.0 SP2 and their resolution. In the previous posts we have seen Installation, Configuration, Managing the WSUS 3.0 SP2. Before we start troubleshooting WSUS issues, lets take a look at some of the log files created by WSUS server.
WSUS Log Files -WSUS setup creates the following four log files that can help you diagnose problems with setup. These log files are located in the %temp% folder of the user who installed the WSUS software.
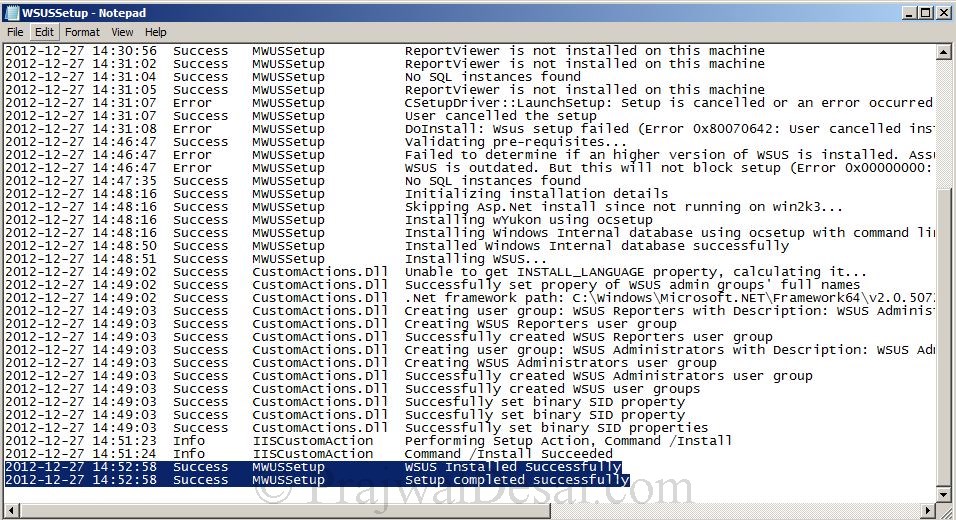
- WSUSSetup.log: The status of each of the component installations that are performed during WSUS setup is logged to this file. You can check this log to see whether any component installation failed. If you see a failure, check the corresponding log to see what went wrong during the installation of that component.
- WSUSSetupMsi_timestamp.log: This log file is generated by MSI for WSUS component setup. Before it invokes custom or standard actions, Windows Installer logs that information to this file. The return values from the custom actions are also logged in this file.
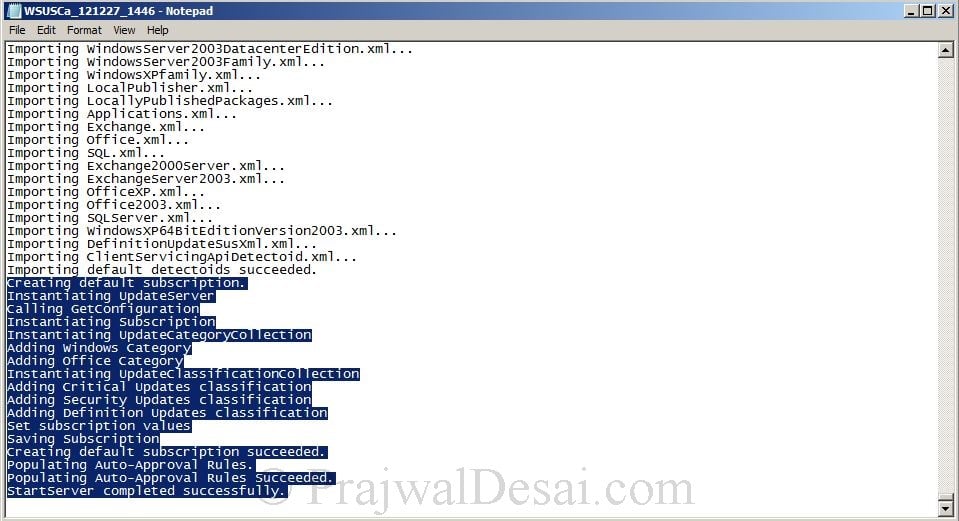
- WSUSCa_timestamp.log: This log file is used by custom actions. Errors that occurred while executing any custom actions in WSUS component or BITS setup are logged in this file.
- WSUSWyukonSetup_timestamp.log: This is the log file for Windows Internal Database setup. All Windows Internal Database installation and uninstallation information is logged in this file.
Apart from these log files, there are 2 more log files that are really important. These log files are located in WSUSInstallationdriveLogFiles.
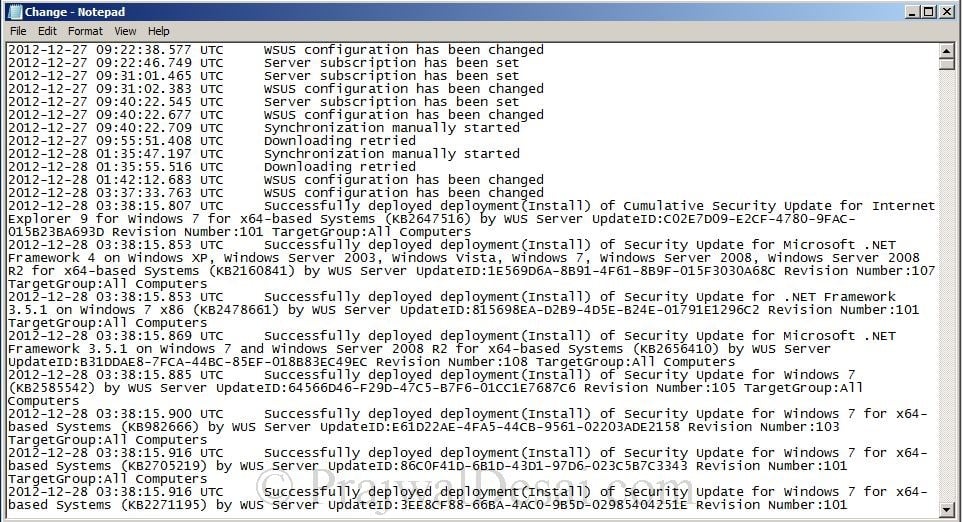
Change.log – When any change or modification is done to the WSUS server, the changes are logged in this file. It also provides information about the WSUS server database information that has changed.
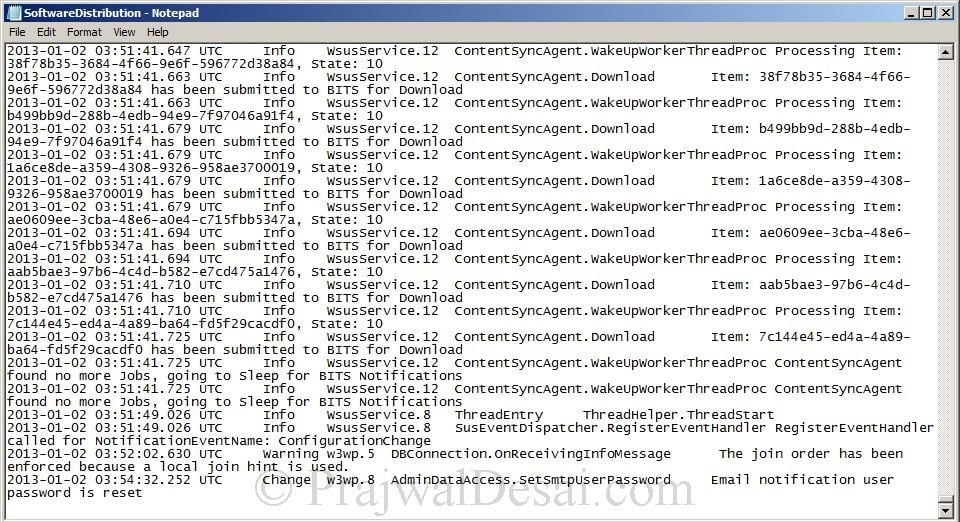
SoftwareDistribution.log – Provides information about the software updates that are synchronized from the configured update source to the WSUS server database.
Important Note – Microsoft has released an update KB2734608 for WSUS 3.0 SP2. This update lets servers that are running Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) 3.0 SP2 provide updates to computers that are running Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012.
This update fixes the following issues:
- Installation of update 2720211 may fail if Service Pack 2 was previously uninstalled and then reinstalled.
- After you install update 2720211, health monitoring may fail if the WSUS server is configured to use SSL.
Common issues related to WSUS 3.0 Sp2 and troubleshooting :
1) WSUS Client Computers are not installing Updates – If the WSUS client computers are not installing updates, then check the DCOM configuration. On the client machine, click on Start, Run, type “dcomcnfg” (without quotes), Component Services window will appear. In the left pane under Console Root, expand Component Services, expand Compoters, right-click My Computer, and then click Properties. Click the Default Properties tab. Make sure that EnableDistributed COM on this computer is selected and Default Impersonation Level is set to Identify.
2) Client Computers Not reporting to WSUS Server :- If you have configured client computers for a particular WSUS server, but they have not reported over a period of days, use the following procedures to isolate and repair the problem
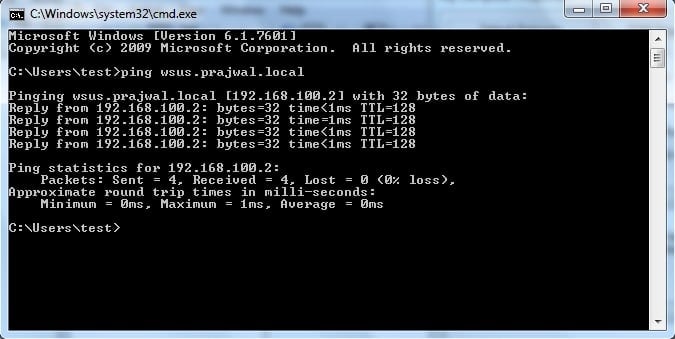
First check the connectivity between the client computer and WSUS server. You can use the ping utility to check connectivity.
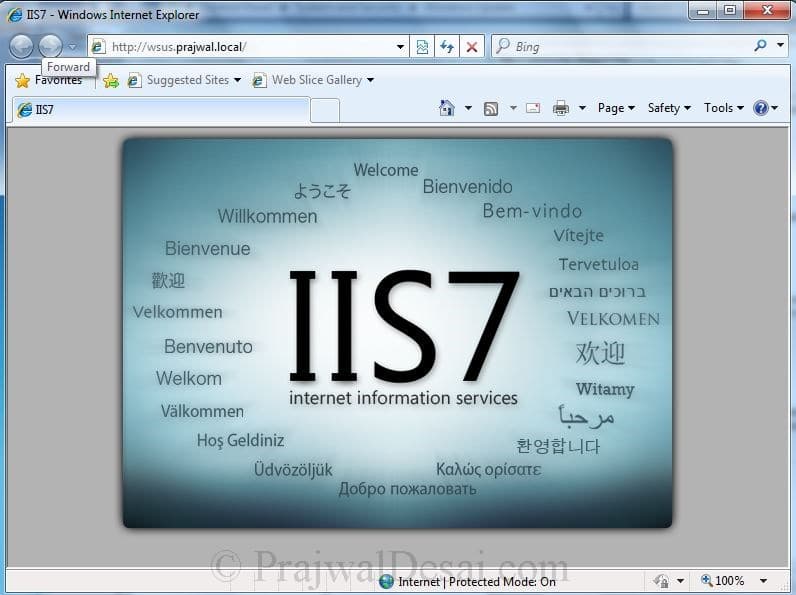
Contact the WSUS HTTP server by providing the servername:port number. open the Internet Explorer and type http://wsusservername:portnumber. You must see the IIS version on the page.
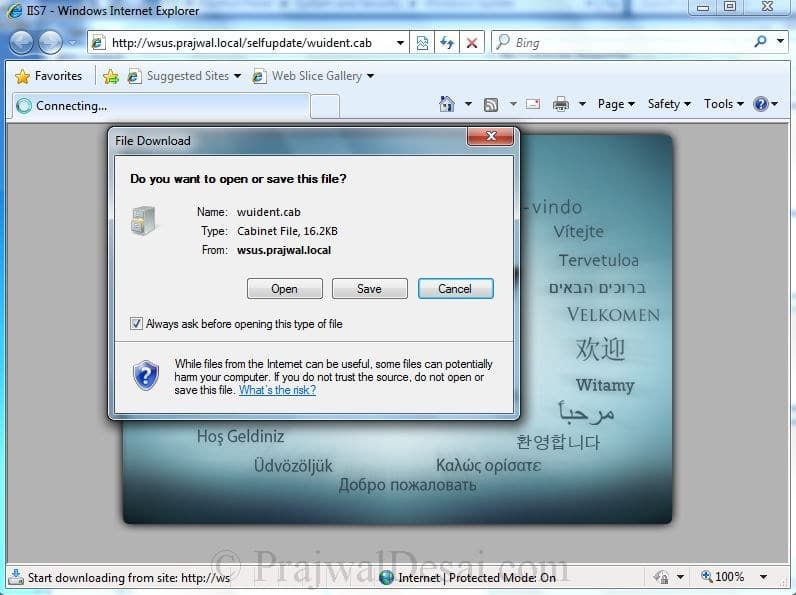
Verify the existence of the self-update tree. In an Internet Explorer address bar, type: http://WSUSServerName/selfupdate/wuident.cab. If the WSUS server is functioning properly, you should see a File Download window that asks you whether to open or save the file.
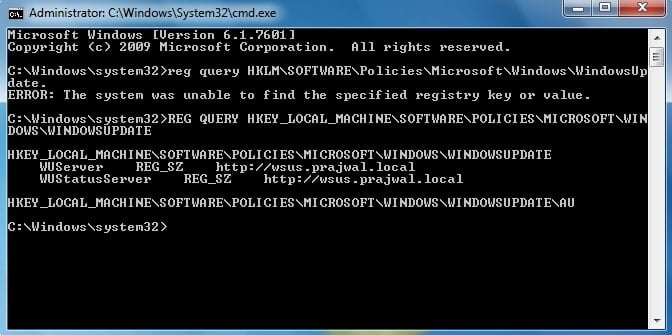
Troubleshoot the Automatic Update client – On the client computer, run the command prompt as administrator, type the following registry query – reg query HKLMSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdate.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdate
WUServer REG_SZ http://WSUSServerName
WUStatusServer REG_SZ http://WSUSServerName
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU
If you don’t find the above output or if the query returns the error, “The system was unable to find the specified registry key or value,” Automatic Update has not been configured on this computer.
Resetting the Automatic Update client :- You can try resetting the automatic update client on the client machine. Open the command prompt on the client machine, type the command – wuauclt.exe /resetauthorization /detectnow. Wait for 10 minutes for detection cycle to complete.
Issues related to BITS – Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) is the service that is used by WSUS to download updates from Microsoft Update to the main WSUS server, and from WSUS servers to their client computers. BITS also supports the transfer of files between peer computers in a domain.
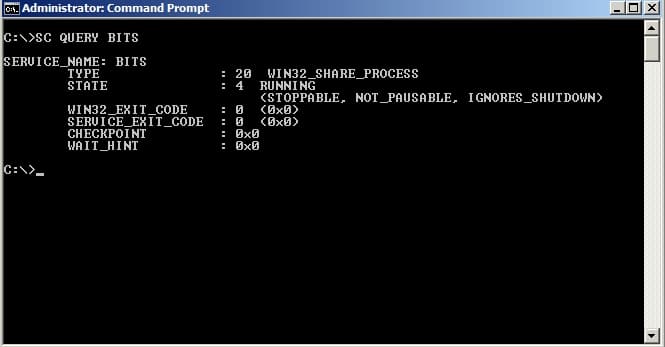
To check whether BITS is running, on the WSUS machine open the command prompt and type the command SC QUERY BITS (can be in lowercase also). We see in the output that BITS is running.
If the BITS Service is not running, then the output should look like this. Note that the STATE is STOPPED.
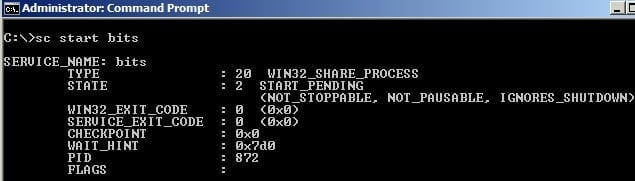
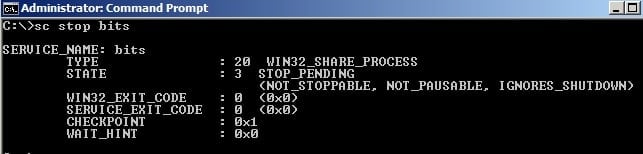
You can start or stop the BITS using the commands “SC START BITS” or “SC STOP BITS“.

Prajwal Desai is a Microsoft MVP in Enterprise Mobility. He writes articles on SCCM, Intune, Configuration Manager, Microsoft Intune, Azure, Windows Server, Windows 11, WordPress and other topics, with the goal of providing people with useful information.
Table of Contents
- Background
- Tips
- What is WSUS
- Inner-workings
- Requirements
- Best-Practices
- Logging
- Coming to a conclusion
- Example
- References
Background
An issue with WSUS on Windows Server 2016 which resulted into computers not reporting correctly to WSUS.
Even when you think having configured everything correctly because computers where connecting to WSUS (they targeted the right WSUS groups from the Group Policy in the WSUS Console), they where not reporting their status to WSUS.
Tips
However many don’t realize this, the most effective way to resolve issues is to understand the problem.
- Don’t just start to search the web blindly, get to know the (basic) inner workings of an application
- Locate all the logging, many applications have documented default logging locations
- If necessary, increase logging. Many applications have options to add information to logging.
- Check if requirements are met
What is WSUS
WSUS is largely built on IIS (Microsoft Internet Information Services), .NET Framework and MMC (Microsoft Management Console).
It uses WID (Windows Internal Database) or Microsoft SQL Server as its database engine. It acts the same way as the publicly available Windows Update, but with WSUS you are able to deploy updates to your systems at your own pace and compliance requirements
. Off course you are able to offload your internet connection by downloading your updates locally, but that never was my primary concern.
You can even create an Internet-facing downstream server, so that your systems download your own approved updates even outside your office(s).
This way you keep your systems up-to-date and/or secure (which off course is largely recommended), without your systems being incompliant to your own requirements.
Inner-workings
Figure: Overview of the WSUS process
Source: Microsoft Corporation —
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc539281.aspx
This figure made by Microsoft shows how WSUS works.
Requirements
In the official Deployment Guide made by Microsoft, the first step it says is to ‘plan’ your deployment.
Immediately followed by requirements. First check if requirements are met (Reference 1).
In many cases the requirements are never checked when implementing a solution.
Even when you deployed it yourself, dare to second-guess yourself!
Depending on IIS, .NET Framework and SQL/WID, WSUS can actually get issues from configuration problems of these services.
Make sure you don’t just check WSUS, check all the parts that make WSUS.
For this the requirements are important, because these services are a requirement for a reason: they are important to WSUS its architecture.
Best-Practices
Best practices are never a requirement.
It can make sure an application/service runs at its best, but only requirements are needed for an application/service to run normally.
Logging
Logging you can find in the following locations:
Reporting to Windows Server Update Services on Client: C:WindowsSoftwareDistributionreportingevents.txt (this file is always there – even when using public Windows Update)
Log of retrieving updates on Client: Get-WindowsUpdateLog (generates a log file on your desktop from Event Tracing for Windows)
IIS on Server: c:inetpublogfiles (or check the inetpub location in IIS)
In the example I’ve set I said that computers had issues reporting.
I knew they connected to WSUS (otherwise group-targeting wouldn’t have worked), however they where not reporting status to WSUS.
This has led for me to check the reportingevents.txt on the client, since Windows Update was connecting to WSUS, just not reporting to it.
This is an example how you can use logging to support your first theories about the problem itself.
Coming to a conclusion
Coming to a conclusion with major WSUS issues can be a bit of a struggle.
WSUS is a complex product, reliant on many technologies.
A conclusion can’t be made before you know where the issues lie:
On the client or the server
In IIS or maybe SQL.
Make sure you know the issue, there always has to be a place where some error is reported in logging.
Example
However targeting worked (computers where placed in the right Computer folders in WSUS), computers wouldn’t report.
When I looked into the ReportingEvents log in C:windowsSoftwareDistribution folder, it showed a error “Windows Update Client failed to detect with error 0x8024401c”.
However this error wasn’t consistent (sometimes it did succeed, but it mostly didn’t)
It looked rather odd.
Browsing the web more people are talking about issues in IIS.
So I compared the Advanced configuration of the WSUS app pool in IIS (server 2016) to an old environment I have built (2012R2), I saw it had an Private Memory Limit of 1.8GB.
Changing this to 0 (unlimited), computers immediately started reporting.
References
- Requirements by Microsoft for WSUS (Chapter 1.1 Plan your WSUS Deployment — Review considerations and requirements) —
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-server-update-services/plan/plan-your-wsus-deployment#BKMK_1.1
- Troubleshooting IIS issues https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/943891/the-http-status-code-in-iis-7-0-iis-7-5-and-iis-8-0
- How to read the Windows Update Log File https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/902093/how-to-read-the-windowsupdate-log-file
- Changing the inetpub location
https://blogs.iis.net/thomad/moving-the-iis7-inetpub-directory-to-a-different-drive
Hello All,
Thanks for joining me here, Today I want to talk about troubleshooting the WSUS 3.0 SP2 server. So, I will be discussing the WSUS server troubleshootiong and some of the resources in troubleshooting the WSUS. Please note that we are discussing the server side troubleshooting and not the client side.
So, If we you have issues with your WSUS server You are at the right place.
Information we should collect before we start troubleshooting the WSUS.
- Event Viewer: Application: Source: Windows Server Update Services
- Background Intelligent Transfer Service
- Application Log Event ID 364 (download failures)
- SQL ERRORLOG %windir%SYSMSISSEEMSSQL.2005MSSQLLog
- C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesLogFilesSoftwareDistribution.log
- C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesLogFilesChange.log
- %windir%Windowsupdate.log – on WSUS client computers.
- IIS Logs %Windir%System32LogfilesW3SVC1 for “Default Web site” W3SVCXXXXXX for “WSUS Administration Site” XXXXXX will be a random number you can locate by looking in IIS under Web Sites, It will be listed as the ID:
Always check the application log to determine if there are errors being generated by WSUS.
- You can force WSUS to report its current health by running “wsusutil checkhealth” then check Application logs for an update.
- Verify http://servername/iisstart.htm can be browsed
- If you cannot see this page, it’s a big indicator that there is something wrong with IIS itself, at this point you’ll need to troubleshoot IIS or engage an IIS engineer for assistance.
- If you can get to the “under construction” page, the next step is to check if asp .net is working http://<WSUSSERVERNAME>/simpleauthwebservice/simpleauth.asmx
NOTE: If you are using SSL, verify you can browse to the above sites without any cert warnings.
Please remember you’ll have to check the above sites with the exact policy using for the WSUS clients, the certificate should contain either the hostname or the FQDN, whichever its using, make sure you enter the correct value when testing if SSL is functioning correctly.
Review IIS logs to verify clients are reaching the server to determine exactly what error code is being returned to the client. You can confirm the IP address, or look at the error code.
If you do not see the client IP address in the IIS logs after trying to sync from the Client (wuauclt/detectnow), the issue may be related to connectivity to the server and you may want to get a network trace of the client/server sync.
For a list of IIS status codes, please check the following KB
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/318380
Aspnet_regiis –I sometimes fixes errors related to .net framework issues.
C:WINNTMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv2.0.50727>aspnet_regiis –i
WSUS IIS Default Permissions are outlined at the following Location:
A lot of WSUS troubleshooting is done within IIS permissions:
All the following sites should be Anonymous Using IUSR_%computername% to access.
· ClientWebService
· DssAuthWebService
· ReportingWebService
· ServerSyncWebService
· SimpleAuthWebService
· Selfupdate
· Content
The following site should be set to Integrated and Digest Authentication:
· ApiRemoting30
A lot of times folks apply a custom security template to either their domain policy or the local computers. If they do lock down the computer, there is a minimum amount of user rights which IIS needs in order to function correctly. There is a support document which discusses the minimum requirements for IIS to function at the following location:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/812614
Synchronization Troubleshooting
Determine what the WSUS server is syncing with (USS, MU)
Review SoftwareDistribution log.
Review Synchronization history in WSUS admin console, there will be a link to the failure
Quick Fixes for synchronization issues:
One common issue with upstream downstream server synchronizations occurs when the upstream server in an USS/DSS hierarchy is rebuilt. It’s possible the downstream server may have content approved on it which is no longer available on MU, when the DSS attempts to sync with the USS and attempts to report status on this update ID which is not present on the USS, it may cause the synchronization to fail.
In this scenario, the best way to resolve the issue is to make the USS a temporary DSS of the existing DSS. Perform synchronization, once it completes, set the USS back to sync with MU and test the sync between the USS and DSS to verify they can sync.
From a WSUS perspective, Bitsadmin is only by a WSUS server to download content from either MU or, an upstream server. A WSUS client uses it to download content from the WSUS server, or from MU.
Mis-configuration of DSS (multi language updates cause USS to download a LOT of content)
Change default view in updates to show File Status to check on an update state
Event ID 364 in Event Viewer
Bitsadmin /list /verbose /allusers>c:bits.txt
This will dump out all the active bits jobs with verbose details. If there is a transfer error you will be able to see it in the output. You can also determine what updates are downloading by reviewing the verbose bits log. (this is helpful for troubleshooting multi – language update issues)
Bitsadmin /reset /allusers
Clears all bits transfer jobs.
Bitsadmin /monitor /allusers
Opens a 5 second refresh window which monitors all active bits jobs, and shows their current state: I.E. TRA – Transferring , QUE – Queued for Trasfer, SUS – Suspended Job
WSUSUTIL Command Line
wsusutil checkhealth
wsusutil listinactiveapprovals
wsusutil removeinactiveapprovals
wsusutil healthmonitoring
wsusutil movecontent
wsusutil reset
wsusutil usecustomwebsite true/false
RENAMING WSUS DB TO ANY OTHER NAME IS NOT SUPPORTED
WSUS 3.0 sp1 comes with a command line utility similar to OSQL to perform maintenance against the database, this utility provides no feedback in the cmd window. The tool is located at C:Program FilesUpdate Servicessetupexecutesql.exe.
Since this tool has little feedback and fairly confusing to use. It his highly recommended you download and install SQL Management Studio Express.
In order to connect to the Windows Internal Database (WIDS) instance, you will need to use Named pipes. You cannot connect using %computername%<instancename> network connections to WIDS are disabled only the following method works:
.pipeMSSQL##SSEEsqlquery
SQL Error Log
By default the Windows Internal Database SQL error logs are at the following Location:
%windir%system32sysmsisseemssql.2005MSSQLLOG
The “current” log is ERRORLOG with no extension.
HOW TO REMOVE WSUS
Remove WSUS3 x86
MsiZap.exe T {2C0D7E35-EE6E-4dc7-BA13-2C68AEDEB59D}
Remove WSUS3 x64
MsiZap.exe T {77846B52-14C9-4fc4-BE63-FE06AF501442}
sc delete wsuscertserver
delete %windir%system32psfsip.dll
http://download.microsoft.com/download/e/9/d/e9d80355-7ab4-45b8-80e8-983a48d5e1bd/msicuu2.exe
Troubleshooting Disconnected Networks:
bitsadmin /list /verbose /allusers >c:bits.log
Most times these issues occur when content is missing during import process or DSS misconfigured to request content not present on USS
· wsusutil reset
· Purge bits jobs “bitsadmin /reset /allusers”
Hope that helps.
| title | description | ms.topic | ms.assetid | ms.author | author | manager | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WSUS Messages and Troubleshooting Tips |
Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) article — Troubleshoot using WSUS messages |
article |
9f6317f7-bfe0-42d9-87ce-d8f038c728ca |
jgerend |
JasonGerend |
mtillman |
01/11/2023 |
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
This article contains information about the following WSUS messages:
-
Computer hasn’t reported status
-
Message ID 6703 — WSUS Synchronization Failed
-
Error 0x80070643: Fatal error during installation
-
Some services aren’t running. Check the following services […]
Computer hasn’t reported status
This message is generated in the WSUS console when a WSUS client computer doesn’t send information to the WSUS server to indicate its current update state. This issue is typically caused by the WSUS client computer, not the WSUS server.
The most common reasons are:
- The computer has lost connectivity to the network:
- The network cable is unplugged.
- An intervening network cable is faulty.
- The computer has a faulty network adapter.
- The network port to which the computer connects has been disabled.
- The wireless adapter is unable to associate with and connect to the corporate wireless access point.
- The computer is turned off. (It has been shut down or is in sleep or hibernation mode.)
Message ID 6703 — WSUS Synchronization Failed
Message: The request failed with HTTP status 503: Service Unavailable.
Source: Microsoft.UpdateServices.Administration.AdminProxy.createUpdateServer.
When you attempt to open Update Services on the WSUS server, you receive the following error:
Error: Connection Error
An error occurred trying to connect to the WSUS server. This error can happen for a number of reasons. Please contact your network administrator if the problem persists. Click the reset Server Node to connect to the server again.
Attempts to access the URL for the WSUS Administration website, for example http://WSUS01:8530, fails with the error:
HTTP Error 503. The service is unavailable
In this situation, the most likely cause is that the WsusPool Application Pool in IIS is in a stopped state.
Also, the Private Memory Limit (KB) for the Application Pool is probably set to the default value of 1843200 KB. If you encounter this problem, increase the Private Memory Limit to 4 GB (4000000 KB) and restart the Application Pool. To increase the memory perform the following steps:
- Open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager console.
- Select Application Pools from the Connections pane, then select WsusPool, right-click and select Advanced Settings.
- Set the Private Memory Limit (KB) to 4000000.
- Select OK to apply the setting.
It may be necessary to increase the Private Memory Limit to 8GB (8000000 KB) or higher depending on the environment.
Error 0x80070643: Fatal error during installation
If WSUS was set up using Microsoft SQL Server, this problem occurs because the user who is running WSUS Setup doesn’t have System Administrator permissions in SQL Server.
To resolve this problem, grant System Administrator permissions to a user account or to a group account in SQL Server, and then run WSUS Setup again.
Some services aren’t running
Check the following services are running:
-
Selfupdate: See Automatic Updates Must Be Updated for information about troubleshooting the Selfupdate service.
-
WSSUService.exe: This service facilitates synchronization. If you have problems with synchronization, access WSUSService.exe by clicking Start, pointing to Administrative Tools, clicking Services, and then finding Windows Server Update Service in the list of services. Once you have found the service:
-
Verify that this service is running. Select Start if it’s stopped or Restart to refresh the service.
-
Use Event Viewer to check the Application, Security, and System event logs to see if there are any events that might indicate a problem.
-
-
Web servicesSQL Service: Web services are hosted in IIS. If they aren’t running, ensure that IIS is running (or started). You can also try resetting the Web service by typing iisreset at a command prompt.
-
SQL Service: Every service except for the selfupdate service requires that the SQL service is running. If any of the log files indicate SQL connection problems, check the SQL service first. To access the SQL service, select Start, point to Administrative Tools, select Services, and then look for one of the following:
-
MSSQLSERVER (if you’re using WMSDE or MSDE, or if you’re using SQL Server and are using the default instance name for the instance name)
-
MSSQL$WSUS (if you’re using a SQL Server database and have named your database instance WSUS)
Right-click the service, and then select Start if the service isn’t running, or Restart to refresh the service if it’s running.
-
This post will cover some basic methods to troubleshoot and fix common problems with Microsoft’s Windows Server Update Services (WSUS).
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
WSUS Server Checks
First we’ll cover some things to check and confirm on the WSUS server itself.
Check WSUS Service
The first thing you’ll want to do is check that WSUS is actually running and working as expected.
PS C:UsersAdministrator> Get-Service -name WsusService Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running WsusService WSUS Service
In this instance the WSUS service is reporting as running. If it’s not you can run the ‘Restart-Service -name WsusService’ to attempt to restart it. This service runs as the Network Service user by default.
Check IIS Service
Additionally we need to ensure that the W3SVC service is running which is IIS, as this is the service that actually listens for incoming connections on TCP ports 8530 for HTTP and 8531 for HTTPS. This service runs as the local system account by default.
PS C:UsersAdministrator> Get-Service -name W3SVC Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running W3SVC World Wide Web Publishing Service
Again if this service is not running, try the ‘Restart-Service -name W3SVC’ command to restart it. Once it’s running, we can use the netstat command to confirm that the WSUS server is correctly listening for incoming traffic on these ports as demonstrated below.
PS C:UsersAdministrator> netstat -an | findstr 8530* TCP 0.0.0.0:8530 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING TCP 0.0.0.0:8531 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING TCP [::]:8530 [::]:0 LISTENING TCP [::]:8531 [::]:0 LISTENING
Here we can see that our WSUS server is indeed listening on both 8530 and 8531 on both IPv4 and IPv6, so it looks good in that regard.
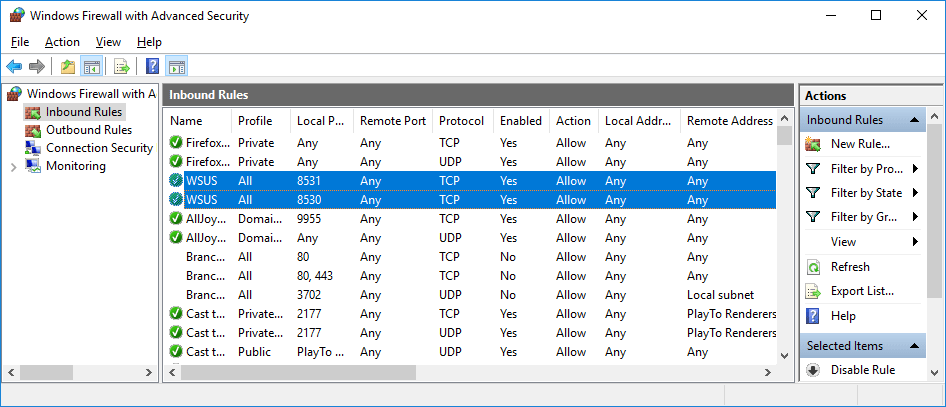
Check Port Connectivity
Just because the WSUS server is listening for connections on the correct ports does not mean that your client machines are able to connect in. By default Windows firewall will be running on the WSUS server, however when you installed WSUS it would have automatically configured two inbound rules called “WSUS” that allow both TCP 8530 and 8531 through, as shown below.
Check that these allowed inbound rules are still in place, and if not either enable them or create new ones as needed.
Check Log Files
Finally if everything on the server side is looking good, take a look at the WSUS log files. If you find any specific error messages here they should be detailed enough for you to perform further investigation (aka stick the error into Google).
- C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesLogFilesChange.log – This file contains information about things that have changed in WSUS, it may be useful for seeing any recent changes that have taken place and caused the problem you’re having.
WSUS Client Checks
Now that we have confirmed that things look good from the perspective of the server we’ll perform some checks from the client, that is the Windows computer that connects to the WSUS server to download updates from.
Check Windows Update Service
In order for the Windows client system to actually perform Windows update, the wuauserv service should be running. If this service is not running, Windows update will not be able to run so restart it if required. This service runs as the local system account by default.
PS C:UsersAdministrator> Get-Service -name wuauserv Status Name DisplayName ------ ---- ----------- Running wuauserv Windows Update
Check Port Connectivity
As we have confirmed that the WSUS server is both listening on TCP ports 8530 and 8531 with appropriate Windows firewall rules, we will now confirm that we can connect to these from the client system. By default Windows firewall allows all outbound traffic, so by default Windows firewall on the client system should not prevent the outbound connectivity unless you’re running custom rules.
Additionally this does not cover any other firewalls that you may be running between the client and WSUS server, so check these are also configured with appropriate rules if you have them.
My favourite way to quickly test port connectivity in Windows is with the telnet client which must first be installed. Once installed it’s as simple as specifying the WSUS server and the port that you want to test, as shown below.
PS C:UsersAdministrator> telnet wsus.example.com 8530
This can be run through either Command Prompt or PowerShell. If it is successful, the screen will go blank. You can quit the telnet client by pressing the Control and ] keys, followed by typing quit and pressing enter.
For further information on how to test port connectivity, see our guide on pinging ports.
Alternatively you could also try to load the http://wsus.example.com:8530/Selfupdate/ (replacing wsus.example.com with your own WSUS server) page from a clients browser, if successful the page should just be plain white with no source. If you get some other error connecting then this may indicate a problem.
Check Group Policy
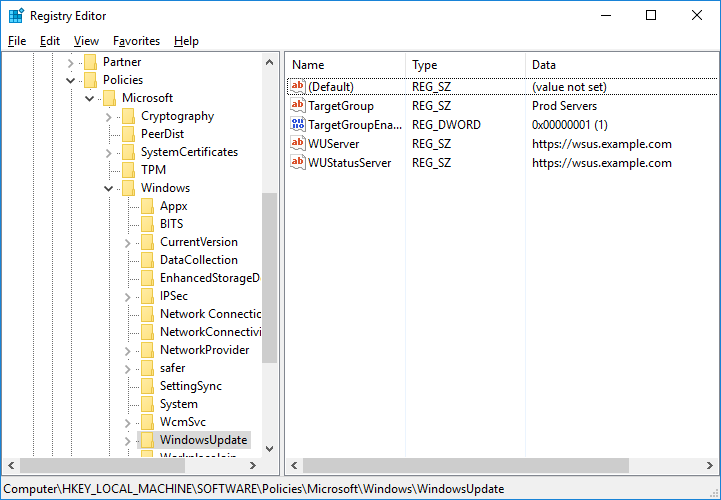
If the connectivity is looking good then you may next want to confirm the correct group policy is actually being applied to the client that is having problems updating. We can view the Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) with the gpresult command, as shown below. The /r parameter is used to show the summary data only.
Applied Group Policy Objects
-----------------------------
Default Domain Controllers Policy
Default Domain Policy
WSUS
We can see that our ‘WSUS’ GPO is indeed applied to this client computer that we ran gpresult on.
We can take this a step further and also check that the registry entries have been set as per the GPO. In the image below we are looking at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdate which shows us the name of our specified WSUS server and target group that are set in the WSUS GPO.
Check Log Files
Finally if everything on the client side is looking good, take a look at the Windows update log files. To generate these, run the ‘Get-WindowsUpdateLog’ PowerShell cmdlet. This will write the WindowsUpdate.log file to C:Users<user>Desktop
Summary
The information here should give you some ideas of things to check when you encounter problems with WSUS so that you can fix common issues. The important things to remember are the location of the log files so that you can quickly identify what the problem actually is and then investigate further from there.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
Windows System Update Services — локальный сервер для развертывания обновлений продуктов Microsoft. Про агента обновления отдельная статья.
Содержание
- 1 Установка
- 2 Перенос базы данных WSUS
- 2.1 Без изменения расположения файлов базы
- 2.2 С изменением расположения файлов базы
- 3 Перемещение кеша обновлений
- 4 Сжатие кеша обновлений
- 5 Развертывание Internet Explorer
- 5.1 IE7 или IE8
- 5.2 IE9
- 6 Где искать логи сервера
- 7 Ссылки
Установка
Windows System Update Services 3.0 устанавливался на старый кэш, который живет в D:WSUS. О том как сохранить старую базу — немного ниже. Сразу скажу, что файлы хранилища БД следует переименовать или как либо приныкать, так как при установке они будут затёрты!.
- ставим винду на диск C: как обычно, при разбивке диска следует предусмотреть не менее 1 ГБ места под WSUS
- обновляем винду до sp2 (у меня был Windows 2003 Web Edition, после установки СП придётся ребутнуть мршину)
- ставим dotnetfx.exe — .NET Framework версии 2.0 или выше
- ставим ReportViewer.exe — он потребуется для просмотра интерактивных отчетов
- ставим WSUS3Setupx86.exe следующим образом:
- запускаем ексешник, читаем-принимаем лицензию
- выбираем полную установку
- выбираем размещение хранилища в D:WSUS — требуется гигов 10, ну, минимум 6, но у меня за 12 зашкалило.
- выбираем размещение базы в D:WSUS — хочет 2 гига, по началу в гиг укладывается вроде
- выбираем рекомендуемый дефолтовый IIS вебсайт на 80 порту
- далее жужжит установщик — успеем покурить…
- после установки автоматом запускается мастер…
- к программе не присоединяемся — снимаем галку
- синхронизируемся прямо с мелкософтовым сервером
- прокси у нас нет (сидим за NAT’ом)
- жмем Start Connection для получения списков обновлений — это надолго…. прием идет редкими небольшими порциями, база медленно растет (примерно метр в минуту)
- выбираем обновления только на русском (по дефолту в 2003 выбраны все языки!)
- выбираем обновляемые продукты — нам нужны: Windowc Vista, XP и Office2007
- выбираем сервиспаки, критические обновления и обновления безопасности, остальное по усмотрению
- выбираем интервал обновлений — раз в день по ночам
- оставляем галки на «запустить консоль» и «приступить к начальной синхронизации»
- если не лениво — на следующей странице можно почитать маны и нажать «финиш»
- запустилась консоль
- наблюдаем за ленивым прогрессом синхронизации
- создаем группы — по номерам комнат, чтоли…
Имеет смысл, когда сервер обновлений просто переезжает с одной машины на другую или когда на диске вдруг закончилось место.
Помимо того, что далее, замечу, что есть в паре таблиц имя и полное доменное имя сервера. Можно ли без правки — фик знает. Как искать… интуитивно.
Без изменения расположения файлов базы
Возможно, есть какой то другой способ, более правильный, но у меня сработал этот.
В целом, операция не сложная, но как оно пойдёт на разных серверах — я не в курсе. При переносе с Windows Server 2003 Web Edition Eng 32-bit на Windows Server 2008 R2 Rus 64-bit проблем у меня не возникло. В моём случае кажется изменилась версия сервера (по крайней мере, в имени юзера вместо 2005 стало 2008).
Действовал в таком порядке.
- На обоих серверах остановил службу Windows Internal Database (MICROSOFT##SSEE).
- Переименовал два файла SUSDB.mdf и SUSDB_log.ldf в папке назначения C:WSUSUpdateServicesDbFiles (потом их можно будет удалить).
- Скопировал те же два файла со старого сервера в папку нового сервера.
- Установил для скопированных файлов владельца и задал необходимые привилегии доступа, как было на старых.
- Запустил на новом сервере ранее остановленную службу Windows Internal Database (MICROSOFT##SSEE).
- Запустил в консоли оснастку сервера обновлений, при этом выскочила ошибка недоступности сервера с предложением выполнить сброс серверного узла.
- Убедившись, что настройки, компьютеры и обновления соответствуют тому что было на старом сервере, удалил ранее переименованные файлы.
С изменением расположения файлов базы
Файлы SUSDB.mdf и SUSDB_log.ldf живут не сами по себе, с ними непосредственно WSUS не работает. С этими файлами работает Microsoft SQL Server. Соответственно, для переноса понадобятся какие-то средства управления этим самым Microsoft SQL Server. Имеется графическая среда SQL Server Management Studio.
Перед перемещением базы следует остановить службу Update services и запустить ее после окончания операций с файлами БД.
При запуске SQL Server Management Studio следует использовать:
- Тип сервера: Компонент Database Engine
- Имя сервера: \.pipeMSSQL$MICROSOFT##SSEEsqlquery
- Проверка подлинности: Проверка подлинности Windows
После успешного подключенияк SQL-серверу следует найти в дереве слева базу данных SUSDB. На ней правый клик -> Задачи -> Отсоединить…. Откроется окошко, где можно выбрать опции отсоединения. Ну и нажать ОК. Если отсоединение завершилось успешно, то БД должна пропасть из дерева слева и должно выскочить окошко с предупреждением о недоступности БД.
Если отсоединение завершилось неудачно, то в окне отсоединения следует обратить внимание на количество активных подключений. Служба Update services в моем случае давала три активных подключения — до остановки службы было пять, а после — два. Кто конкретно держит эти два подключения, можно гадать. Одно, вероятно, это консоль SQL Server Management Studio, а вот по поводу второго мыслей нет. Тем не менее, если Update services точно остановлена, то отсоединение можно произвести с установленной галочкой Удалить соединения.
После успешного отсоединения можно переместить файлы в новое расположение (или скопировать файлы с другого сервера)
Затем на пункте Базы данных в дереве слева необходимо сделать правый клик и выбрать пункт Присоединить. В открывшемся окошке жмакнуть Добавить и выбрать файл SUSDB.mdf в новом месте расположения. Второй файл подхватывается автоматически, если он рядом. Ну и нажать ОК. База должна появиться в дереве слева.
Перемещение кеша обновлений
В предыдущем разделе я намеренно указал что кеш (или контент сервера обновлений, если так угодно) будет жить на диске C:, в то время как в самом начале он был на D:. Действительно, крошить диск на кусочки не хотелось, и потому на новом сервере сделал только один логический раздел C:. Однако, совсем не достаточно при установке указать новое место расположения. Дело в том, что в базе прописаны абсолютные пути к файлам обновлений. Первое, что пришло в голову — найти какого то клиента этой виндовой БД, и запросом изменить данные. Но правильное решение нашлось достаточно быстро. Из консоли даём команду:
C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesTools> .wsusutil.exe movecontent c:wsus c:logmove.log -skipcopy Изменяется размещение содержимого. Не останавливайте выполнение программы. Перемещение содержимого успешно закончено.
Подробно об использовании команды можно посмотреть в её справке (для тех, кто не в курсе, справку можно посмотреть, запустив команду с ключиком /?). Отчёт же об операции в данном примере сохранён в файле c:logmove.log.
Сжатие кеша обновлений
Кеш обновлений разжирел до безобразия. Мастер очистки сервера почти ничего не чистит. Как таковой, процедуры сжатия кеша нет. Однако, можно прибить всё, что есть. Потом сервер WSUS скачает заново только нужное. Последовательность действий следующая:
- Остановить службу Update Services в консоли управления компьютером.
- Удалить все файлы и директории из D:WSUSWsusContent
- Запустить службу Update Services
- В консоли cmd выполнить команду:
C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesTools>wsusutil.exe reset
- Проконтролировать через некоторое время лог C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesLogFilesSoftwareDistribution.log
Далее сервер будет в фоновом режиме тянуть нужные файлы заново.
Развертывание Internet Explorer
IE7 или IE8
Искать Internet Explorer 7 и 8 следует в классе Накопительные пакеты обновлений или Rollup updates. Там следует найти нужный и одобрить для установки.
Еще инфа по теме: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/946202/ru http://technet.microsoft.com/ru-ru/library/cc985359.aspx
IE9
В левой менюхе правый клик на Обновления -> Импортировать обновления. Откроется браузер и перейдет на Каталог Центра обновлений Microsoft. В строке поиска вбиваем Internet Explorer 9, добавляем нужное в корзину и импортируем. Возможно, придется установить компонент ActiveX.
Где искать логи сервера
Логи работы WSUS пишет в журнал событий Windows — Приложения
Ссылки
- http://www.wikiznanie.ru/ru-wz/index.php/WSUS_FAQ
- http://forum.ru-board.com/topic.cgi?forum=8&topic=14937